Vitamin D, Are You Sure You Are Getting Enough? What exactly is it for? And what happens in the event of a shortage? Let's see the consequences together ...
Don't store avocado like this: it's dangerousVitamin D, Are You Sure You Are Getting Enough? Known for its ability to keep bones healthy and good for the immune system, heart and brain, one deficiency of vitamins of group D can lead to the appearance of various pathologies. But what exactly is vitamin D used for? And what happens in the event of a shortage?
A possible deficiency of this vitamin, evaluated through a specific blood test, must be kept under control, especially in children and if they are over a certain age.
Many studies over the years have shown its importance in the prevention of various diseases including tumors and disorders of the nervous system, but also against some infections. Vitamin D is fat-soluble, so it dissolves in fats, and, unlike other vitamins, it behaves as if it were a hormone, acting on different organs and tissues.
Not everyone knows that:
- we are only minimally able to ensure the need for vitamin D through nutrition and in a way that is not sufficient to meet the needs. It is mostly about foods of animal origin such as fish, milk and eggs or so-called "fortified foods", which therefore indicate the presence of added vitamin D on the label. Among the foods of plant origin, mushrooms are rich in vitamin D
- to acquire a good dose of vitamin D we need to regularly expose ourselves to the sun, every day for at least 20-30 minutes. However, some factors can hinder the production of this substance, such as the use of sunscreen. With this we are not telling you not to protect yourself from the harmful action of ultraviolet rays, but to continue using protective creams in the hottest hours of the day, reserving at least half an hour of time for exposure without cream, but only when the sun it is low and there is no longer the risk of sunburn
- factors that inhibit the absorption of vitamin D are also obesity, air pollution and old age
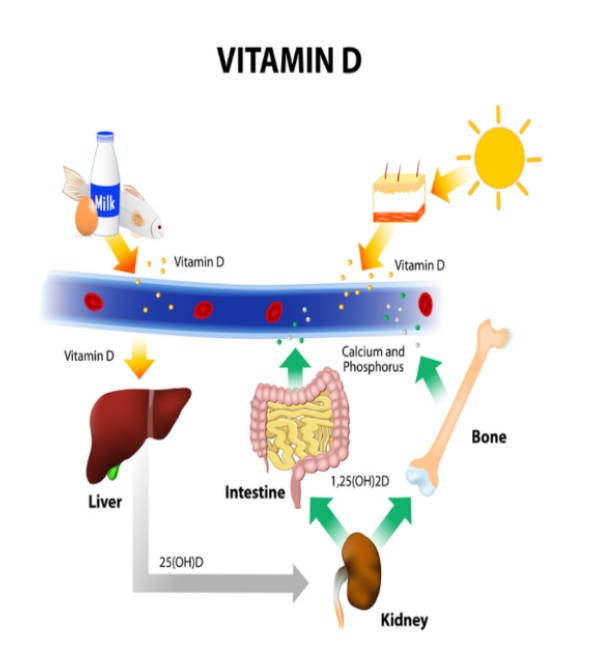
What is vitamin D used for?
Put yourself in the sun that is good for your bones! Grandmothers always say it, sometimes without even knowing it's right there vitamin D the dispenser of all goods: essential for good bone health (it regulates the metabolism of calcium both as far as the absorption and fixation of the mineral in the bones), for the mineralization of the teeth and therefore is essential for growth in the case of the little ones and for the health of the body when it comes to the elderly.
Vitamin D is also useful in the intestinal absorption of other precious minerals for our body, such as phosphorus, and in the regulation of the nervous system. Constant exposure to the sun with consequent production of vitamin D also helps in case you suffer from depression and also serves for the proper functioning of the muscular system, to strengthen the immune defenses and to act as protection against certain types of tumors and diseases such as 'Alzheimer's.
What happens if there is a vitamin D deficiency
There can be many consequences of a vitamin D deficiency. All, however, vary according to age and health conditions. Among the consequences of a shortage:
- Rickets: is one of the most serious and known consequences of vitamin D deficiency in children, due to either a vitamin D deficiency caused by lack of exposure to sunlight or a poor dietary intake. In adults, deficiency of this vitamin can lead to bone deformation, abnormal arching in the lower limbs and spine.
- depression: vitamin D stimulates the production of serotonin, the hormone of happiness.
- Alzheimer's: a study links vitamin D deficiency to the increased risk of getting Alzheimer's, with particular reference to populations living in areas of the world that are not very sunny
- heart risks: Another study shows that low levels of vitamin D could be harmful to the heart
- Multiple sclerosis risk for women: Vitamin D deficiency is also associated with a doubled risk for women of getting multiple sclerosis
- autoimmune diseases: low levels of vitamin D could lead to a higher incidence of autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and type 1 diabetes
Follow your Telegram | Instagram | Facebook | TikTok | Youtube