A team of Swedish researchers has identified a new, very early and more aggressive form of Alzheimer's. The new study
Don't store avocado like this: it's dangerousA team of Swedish researchers has identified a new, very early and more aggressive form of Alzheimer's. The new study
An international team of scientists has discovered a genetic mutation linked toearly onset of Alzheimer's disease, which traced the DNA defect in multiple members of a single family.
Alzheimer's has long been known as a disease that robs the mind, erases memories and destroys the sense of self. Most cases arise after the age of 65. Aside from Alzheimer's dementia that begins sporadically in old age, there are insidious family forms that begin years or decades earlier. Early onset therefore refers to Alzheimer's starting before age 65.
A systematic review
An international team of scientists, led by neurobiologists in Sweden, has identified an extraordinarily rare form of the disease that has so far only been found in one family. This Alzheimer's form is aggressive, rapid and destroys all cognitive functions.
The research showed that the affected individuals were around forty years old at the onset of symptoms and found a very rapid course of the disease.
Researchers found that a mutation accelerates the formation of brain-damaging protein plaques, known as beta amyloid or more simply as Aβ. The plaques destroy neurons and, as a result, nullify the executive functions of the brain itself. (Read also: Found in the brain stem of the youngest air pollution micro particles (linked to Alzheimer's and Parkinson's)
The results
The results came after genetic analyzes, structural biological research, studies on the chemistry of amino acids and proteins, and mass spectrometry to characterize amyloid, the deleterious protein that pervades the brain tissue of mutation carriers.
In the case of the carriers, they all had a deletion in a specific string of amino acids, which are part of the amyloid precursor protein.
The story of the family behind the genetic discovery It started seven years ago in Sweden when two brothers went to a memory impairment clinic at Uppsala University Hospital, where memory problems and loss of sense of direction were assessed. Aged only 40 and 43 at the time, the brothers, sadly, weren't the only ones whose minds were confused and unraveling. Another relative, the cousin their age was experiencing nearly identical symptoms. All were diagnosed with early-onset Alzheimer's disease. (Read also: Former prima ballerina suffering from Alzheimer's listens to Swan Lake and remembers all the choreography)
By the time the two brothers and their cousin arrived at the memory impairment clinic, they were all severely symptomatic. They had trouble speaking and had lost the ability to perform simple calculations.
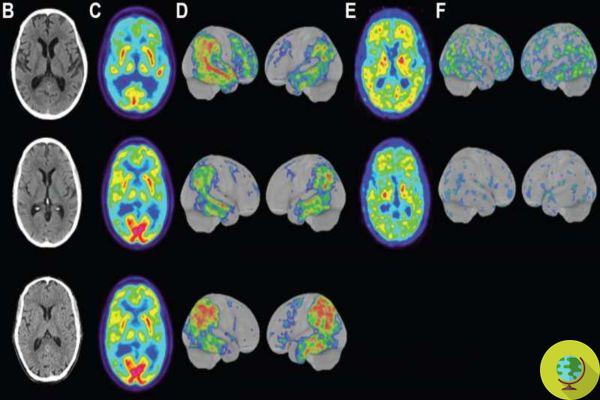
Doctors revealed the hallmarks of Alzheimer's in all three; Brain scans revealed evidence of atrophy in the fronto-parietal and mid-temporal regions of the brain. Scores on the Mini Mental State Examination, an assessment frequently given to older adults to test cognitive abilities, were not only low but were in a range usually seen in older adults with cognitive disabilities.
Researchers have termed this form of Alzheimer's disease as an autosomal dominant, passed on from one generation to the next and which moves rapidly. Symptoms and biomarkers are typical of Alzheimer's disease, with the exception of normal cerebrospinal fluid.
Alzheimer's disease currently has no cure and according toWorld Health Organization (WHO) The disorder is expected to overwhelm global health systems by 2050 due to the inexorable aging of the population.
Follow us on Telegram | Instagram | Facebook | TikTok | Youtube
Photos: Medical Xpress
Could it be interesting for you:
- Pollution and Alzheimer's: Improving air quality reduces risk, now three new studies confirm this
- Lemon peel improves memory (and could help Alzheimer's patients). I study
- From the hallucinogenic tea of shamans, the substance that could revolutionize the treatment of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's