What are the differences between omega 3 and omega 6 fatty acids? Omega 3 and omega 6 are called essential fatty acids
Don't store avocado like this: it's dangerousWhat are the differences between fatty acids omega 3 e omega 6? Omega 3 and omega 6 are called essential fatty acids because it is essential for us to introduce them through our diet since our body does not produce them by itself.
It is important to be able to maintain the correct food thanks to a balanced diet balance between omega 3 and omega 6. You may experience a low intake of omega 3 while there is no such risk with regard to omega 6, since they are much more present in the common diet than omega 3.
Our body has omega 3 and omega 6 polyunsaturated fatty acids available starting from very specific foods which it is important to take into account for a correct dietary intake of these substances. Some foods provide both omega 3 and omega 6 in a balanced way. We refer for example to hemp seeds.
Index
What are omega 3s
Omega 3s are gods polyunsaturated fatty acids considered very important for the prevention of cardiovascular diseases, so much so that their intake is often recommended not only through food but also in the form of supplements. According to epidemiological studies, populations who consume omega 3 in abundance have greater protection from the risk of cardiovascular disease. According to experts, omega 3s have the advantage of reducing the aggressiveness of LDL cholesterol, even if they do not lower blood cholesterol levels.
Read also: OMEGA 3: ALL THE BENEFITS OF GOOD FATS
The sources of omega 3
The main sources of omega 3 are fish and shellfish. However, these sources have the disadvantage of absorbing heavy metals and other contaminants that come into contact with our body through food. This drawback is solved by taking omega 3 in the form of supplements or by choosing the plant sources of omega 3 that we have available.
In fact, omega 3 are not only contained in fish and molluscs but also in linseed, linseed oil and walnuts, which represent the main plant sources of omega 3. Pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, dark green leafy vegetables, soy, tofu and seaweed are sources of omega 3, albeit with a lower intake.
Read also: NOT ONLY FISH: THE 5 VEGETABLE SOURCES OF OMEGA 3
The Scientific Society of Vegetarian Nutrition recommends to take 1 or 2 servings of foods that contain omega 3 every day. One serving is equivalent to 1 teaspoon of linseed oil, 3 teaspoons of flax seed (to be consumed after grinding them, otherwise our body cannot assimilate them and expels them whole) or 30 grams of nights (about 6 nuts).
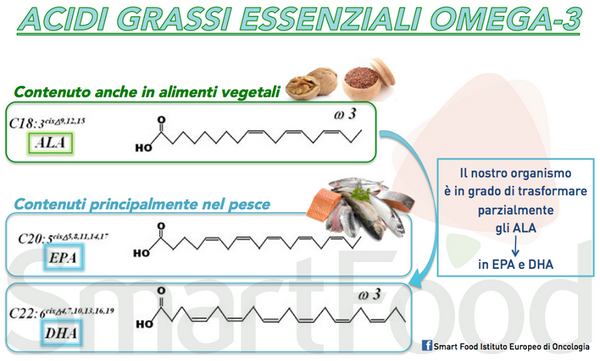
Photo source: European Institute of Oncology

Photo source: European Institute of Oncology
What are omega 6s
Omega 6 are polyunsaturated fatty acids of vegetable origin. I'm considered omega 3 fatty acid antagonists. For this reason, the consumption of omega 3 and omega 6 fatty acids should be balanced. Excessive intake of omega 6 it could prevent our body from enjoying the benefits of omega 3. Both omega 3 and omega 6 are necessary for the proper functioning of our body but we should not overdo the intake of foods rich in omega 6 to avoid a situation from imbalance.
Omega 3 and Omega 6 taken in the right proportions they fight stress, protect the heart and skin and keep blood pressure under control.
The sources of omega 6
Omega 6 are mainly contained in vegetable oils, for example in olive oil, wheat germ oil, sunflower oil, corn oil, sesame oil, peanut oil and the infamous palm oil. Vegetable oils rich in omega 6 are widely used industrially for the production of baked goods and snacks. Consumption should be reduced in order not to unbalance the ratio between omega 6 and omega 3 in our body, which should be of 1 to 5 to really protect the heart.
THU some useful tips for balance the intake of omega 3 and omega 6 with power.
Marta Albè
Read also:
- OMEGA 3: ALL THE BENEFITS OF GOOD FATS
- OMEGA 3 AND OMEGA 6: FATTY ACIDS AT THE BASE OF HUMAN INTELLIGENCE