Homocysteine is an amino acid that if it reaches too high levels in the blood can cause various health problems, especially cardiovascular diseases.
Don't store avocado like this: it's dangerous
High homocysteine, what to do? Everyone knows cholesterol as a possible risk factor for some of the diseases that we frequently incur in these times but few know that there is another marker just as important. This is thehomocysteine, for an amino acid that if it reaches too high levels in the blood it can cause various health problems.
Just like cholesterol, much of the homocysteine that circulates in our body it comes from the metabolism of the foods we eat, in particular from proteins of animal origin. The diet, often lacking in some vitamins (especially those of group B) and a sedentary lifestyle perhaps associated with bad habits such as smoking, or an abuse of substances such as alcohol and coffee aggravate the situation. But also genetic factors, theenvironmental pollution, drugs and some metabolic diseases that may be present can affect homocysteine metabolism.
The problem is that, of a possible imbalance situation, it is difficult to notice since it does not appear initially any symptoms. But slowly the amino acid in excess damages the walls of the blood vessels and it can lead to cardiovascular diseases in the first place. However, too much homocysteine has also been associated with the appearance of other diseases such as Alzheimer's, bone fractures, arthritis, senile dementia and during pregnancy it can lead to fetal malformations.
The only way to evaluate the homocysteine level and possibly intervene is to have the values checked through specific blood tests. The range within which we must fall has been established by the WHO (World Health Organization), we are talking about 13 micro moles for men, 10,1 for women and 11,3 for children under 14. If the sampling shows higher values, it is advisable to intervene immediately by modifying the power supply.
RECOMMENDED AND NOT RECOMMENDED FOODS
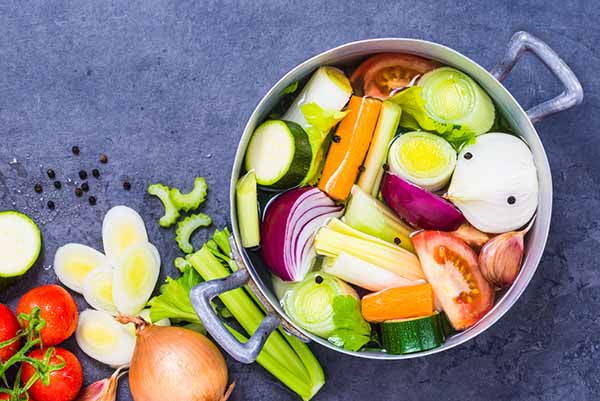
There is a fairly simple system for treating hyperhomocysteinemia cases: take a lot of folic acid (B9). This is because at the metabolic level homocysteine is formed starting from methionine (an amino acid particularly present in animal proteins) but if there are sufficient folate in the blood the situation manages to remain balanced. Green light therefore to all foods rich in folic acid, in particular green leafy vegetables, cruciferous vegetables, fruits which should be consumed as much as possible raw or lightly steamed as folic acid is a vitamin that tends to disperse with high temperatures. HERE you will find all the foods that contain more. The ideal is, as is now recommended by every doctor or nutritionist, eat at least 5 servings of fruit and vegetables every day.
It may be important to associate with a greater intake of folic acid even a little more B12, another essential B vitamin as it supports and supports the work of B9. If it is really not possible to stem the situation of excess homocysteine with food, the doctor may also recommend a daily supplement of 0.5 mg of folic acid.
In case of hyperhomocysteinemia it is good reduce the consumption of animal proteins (especially red meat, fish allowed instead) rather choosing plant-based proteins like legumes.
Read also:
Vitamins: all the properties and foods that contain more of them
Folic acid: foods that contain the most
Vitamin B12: what are the safe sources?
Cholesterol: 10 foods to reduce it and keep it at bay