Meningitis. A disease that cyclically returns to scare. It is an inflammation of the meninges, or the membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. It is important to know what it is, how it is transmitted and the symptoms not to be underestimated.
Don't store avocado like this: it's dangerousMeningitis. A disease that cyclically returns to scare. It is about inflammation of the meninges, or the membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. It is important to know what it is, how it is transmitted and symptoms not to be underestimated.
there various forms of meningitis, some milder others decidedly serious that can even lead to death. Meningitis of viral origin or aseptic meningitis is a mild form of the disease and usually goes undiagnosed as it is easily mistaken for the flu. The situation is very different for meningitis of bacterial origin (fortunately very rare), which must be recognized and treated in time to avoid serious consequences.
Read also: MENINGITIS WHAT IT IS, CAUSES AND HOW TO RECOGNIZE IT
Index
CAUSES OF MENINGITIS
As you will have understood, the causes of meningitis can be different, the disease can in fact appear following the presence of viruses, bacteria and fungi or fungi. Viruses are generally herpesvirus or enterovirus, but there are many others that can trigger so-called aseptic meningitis. This type of disease, however, as already mentioned, is not worrying, it heals in a short time and often you do not even realize you have contracted it.
Bacterial meningitis can arise due to the Neisseria meningitidis (meningococcus), in particular its serogroups A, B, C, W 135 and Y, and pneumococcus. Then there is haemophilic meningitis type B (Hib) which until the 90s was very common in children under the age of 5. But now almost the entire population has developed immune defenses against this type of bacterium.
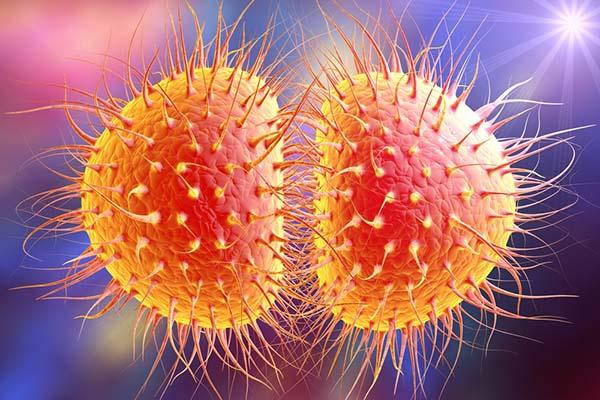 Photo: Neisseria meningitidis (meningococcus)
Photo: Neisseria meningitidis (meningococcus)
Between the risk factors of bacterial meningitis there are age (children under 5, young people between 18 and 24 and older people are more at risk), community life, smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke and other upper respiratory tract infections. Pregnancy is also one of the risk situations, since pregnant women are more prone than others to listeriosis, which in turn can degenerate into meningitis.
There is also a fungal or fungal meningitis which occurs mainly in people who have low immune defenses.
Few people know that many pathogens (including meningococcus and penumoccus) are often present in the pharynx of healthy individuals, do not give any symptoms and do not increase the risk of meningitis.
HOW MENINGITIS IS TRANSMITTED
Meningitis is transmitted via air contact that is, an infected person can pass the bacteria responsible for the disease through breathing, secretions from the nose and throat, kisses but also using objects used shortly before by those who already have meningitis in progress: towels, handkerchiefs, food, glasses and cutlery, toothbrush from teeth, etc.
To be infected it is necessary to be in close and prolonged contact with the infected person or in very crowded environments.
Fortunately the meningococcus is only able to live outside the human body for a few minutes, this is why the disease is not transmitted as easily as it is for other types of bacteria or viruses such as those that cause the flu.
Meningitis it is contagious only in the acute phase symptoms and in the days preceding its onset.
In summary, meningitis is transmitted:
• By air through nose and throat secretions
• You kiss
• Using objects of an already affected person
MENINGITIS INCUBATION
The incubation time may vary depending on the cause of the infection: viral meningitis varies from three to six days, bacterial meningitis from 2 to 10 days.
SYMPTOMS MENINGITIS
Initially meningitis leads to the appearance of very general symptoms that can easily be confused with those of other problems of much lesser severity. They can appear for example headache, fatigue, irritability and nausea.
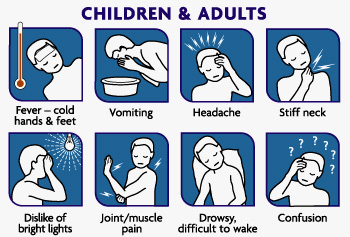
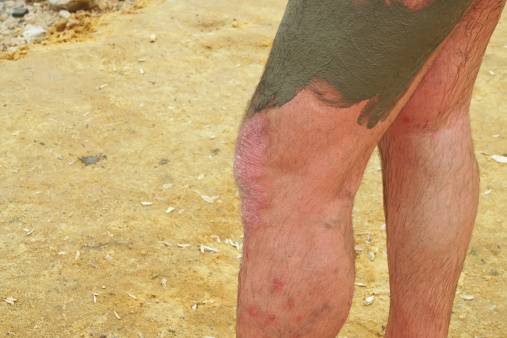
Surely the symptoms that should never be underestimated in case they appear are very high fever (exceeding 40 °) e stiffness in some parts of the corpor, in particular of the nape and extension of the leg. This concretely means that there is so much tension in that area that you can't move as usual. This is a very important wake-up call to report to your doctor right away.
Another thing that should never be underestimated is the appearance of convulsions which, even if it is not meningitis, can still lead to serious consequences. In many cases, meningitis causes a real state of mental confusion in which, in addition to tiredness and drowsiness, it is no longer possible to stay well concentrated, carry out the usual activities or even speak completely correctly.
Another symptom not to be overlooked is a sudden hypersensitivity to light.
Read also: MENINGITIS: SYMPTOMS NOT TO BE UNDERESTIMATED
SYMPTOMS LIGHTNING MENINGITIS
When we talk about fulminant meningitis we mean those cases of meningite batterica (usually gives meningoccco) in which the course of the disease is rapid and acute, precisely fulminant (this is 10-20% of cases) and which can lead to death in a few hours even if appropriate therapy is followed.
The most frequent symptoms of fulminant meningitis are the same as those of meningitis with more moderate courses:
• headache
• fever
• lethargy
• irritability
• nausea
• skin rashes
Those to take more into consideration but they are:
• convulsions
• stiffness in the nape of the neck and leg extension
• sensitivity of the eyes to light
MENINGITIS PROPHYLAXIS
In case of bacterial meningitis treatment must be timely and based on antibiotics. It would be important to identify the responsible strain in order to use specific drugs. If, on the other hand, the meningitis is of viral origin, the situation is decidedly less serious, there is no need to do antibiotic therapy but only collateral to keep the symptoms at bay and it resolves spontaneously within about a week.
Whoever has been to contact with a person with meningitisand must immediately go to the doctor to carry out the routine prophylaxis and thus prevent the appearance of the disease.