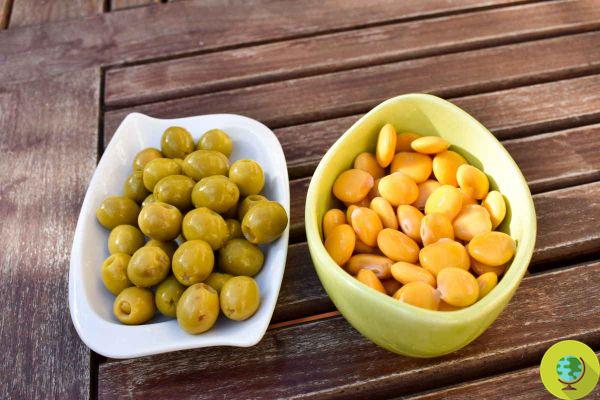
Tarwi, chocho or Peruvian lupine (Lupinus mutabilis Sweet) is a variety of lupine native to the Andes of Peru, Ecuador and Bolivia. In this area of the world it has in fact been known for generations as an important food for sustenance.
Il tarwi, chocho o Peruvian lupine (Lupinus mutabilis Sweet) is a variety of lupine native to the Andes of Peru, Ecuador and Bolivia. In this area of the world it has in fact been known for generations as an important food for sustenance.
In fact, tarwi is a very rich legume protein and has a central role in the nutrition and gastronomy of the Andean countries. This legume helps prevent protein deficiencies that could occur in a rather poor diet.
It is in general a plant of great interest for human nutrition since its protein content is higher than that of soy. Tarwi has been part of the diet of the Andean countries for centuries, even before the Hispanic colonization.
The tarwi is defined a food fromhigh nutritional value, so much so that it is considered a real superfood, as are other foods including, for example, quinoa.
Peruvian lupine is rich in iron, calcium and phosphorus. Its consumption it is recommended for children and adolescents during the developmental age. It is also recommended for mothers-to-be during pregnancy and for new mothers during breastfeeding.
In recent years the importance of this food had been underestimated compared to the past, but now science is also rediscovering it beneficial properties of tarwi as a nourishing and restorative food for our body. Its nutritional characteristics are similar to those of soy. The tarwi forcontains 44,3% protein, compared with 33,4% of soybeans.
Consuming tarwi helps strengthen the immune system, thus preventing infections and contagious diseases. Tarwi, which is grown at an altitude between 2000 and 4000 meters, brings benefits not only to the human body but also to agricultural land, since it contributes to enriching them with nitrogen.
Being rich in fiber, tarwi, like other legumes, is useful for prevent obesity, to regulate bowel functioning properly and to prevent constipation problems. The iron contained in tarwi contributes to the production of hemoglobin and to the transport of oxygen in the blood.
One of the major production areas of tarwi is the La Paz plateau. The cultivation of tarwi in recent years is gaining a strong social value. In fact, its cultivation at a family level is helping the food sustenance of the populations living in the Andean localities.
Tarwi is eaten as a common legume or is ground, once dried, to obtain one flour which is mixed with wheat flour in the artisan preparation of bread. Tarwi is usually used as an ingredient for the preparation of dishes based on Quinoa or amaranth.
Since it is a really healthy food, it is important that the Peruvian communities continue to cultivate it. This is how some associations, including Slow Food, have taken action to protect and encourage the cultivation of tarwi and to promote the local sale of this food, mostly still unknown outside the Andes, in order to provide a form of economic support for farmers' families.
Marta Albè
photo source: twitter
Read also:
The 5 healthiest legumes on the planet
Legumes: herbs, spices and tips to digest them better
Dried legumes: how to use them in the kitchen and beyond