Don't store avocado like this: it's dangerous
Don't store avocado like this: it's dangerous
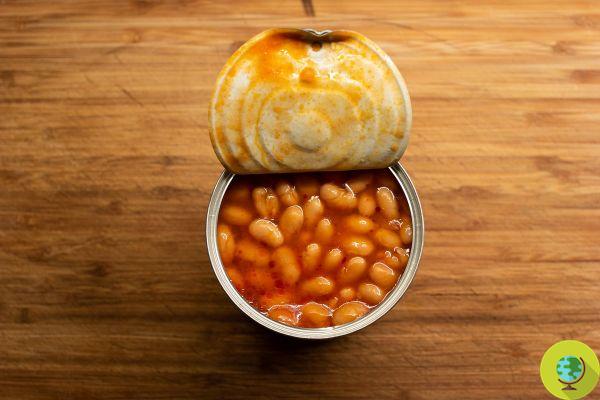
Canned beans are a great and convenient source of plant-based protein, but how are they prepared? And which ones to prefer?
I beans are legumes, plants that produce pods with seeds inside and, according to one search, are an important source of vegetable protein and other essential nutrients, such as iron e folate . But even canned ones retain the same benefits and remain just as healthy? Many people do not recognize canned legumes for their benefits; indeed, we are led to think that they are nutritionally inferior or harmful compared to dried vegetables, especially in case of high blood pressure due to the presence of salt. But is it really so? (Read also: Legumes, the best protein, but canned ones are ok too?)
Index
How are canned beans made?
Canned beans, as well as other legumes, are partially cooked and then canned at high temperature and pressure. In industrial canning, dried legumes are first rehydrated in hot water at about 75-85 ° C; this process kills all microorganisms on the surface of the beans.
They are then treated with food additives, including salt, and canned under high pressure and heat. The studies have shown that thecanning reduces the polyphenol content, i.e. beneficial plant compounds such as vitamins and antioxidants that occur naturally in legumes, such as beans, and can have protective effects on the body.
It has been shown that canning also changes the weight and color of some legumes, and it can slightly reduce the protein content. Manufacturers of canned beans, for example, partially cook the beans and then add food additives and use specific treatments to reduce microorganisms.
Benefits of canned beans
According to a search, people often don't recognize dried or canned beans for their potential role in preventing some chronic diseases. However, some studies have shown how these foods are nevertheless versatile e rich in nutrients, which can reduce the risk of chronic diseases and also offer other benefits for our health.
Here are the main benefits of canned legumes.
Sources of vegetable proteins
Beans are an important source of vegetable proteins and they are a valid substitute for meat, especially in the case of a vegetarian or vegan diet. And even canned ones preserve this characteristic.
Here are the estimated amounts of protein adults should consume per day:
- People under the age of 65: about 0,36 grams of protein per kilo of body weight (0,8 grams per kilogram) - which is about 58 grams of protein for a person weighing 72 kg.
- People over the age of 65: about 0,45 grams of protein per kilo of body weight (1,0 grams per kilogram) - that's 72 grams of protein for a person weighing 72 kg.
Canned legumes can help meet the daily protein requirement; for example, according to one review, 1 cup (171 grams) of canned pinto beans provides 15,4 grams of protein. Additionally, plant-based diets have been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease, 2 type diabetes e metabolic syndrome, and they can also improve brain function.
Sources of dietary fiber
La dietary fiber it is a type of carbohydrate that our body cannot digest. Research has shown that it can help increase satiety, which can promote weight loss and lower blood cholesterol levels.
As reported by USDA, one cup (171 grams) of pinto beans cooked provides 15 grams of fiber, more than half the recommended daily value of 28 grams.
Gut health
It has been shown that legumes are also a prebiotic food, a source of nutrition for the beneficial bacteria that live in the gut. Beans contain compounds with anti-inflammatory and lipid-lowering properties, which means they help reduce inflammation and blood fat levels, respectively, while also supporting a intestinal microbiome diverse and healthy.
The intestinal microbiome is none other than the community of bacteria that live in the intestine; plays an important role in overall health, including weight management. Research suggests it may also protect against development of neurodegenerative diseases.
Cost and convenience
Compared to their dried alternatives, canned legumes are easy to prepare, have a long service life and are relatively economic.
For example, canned beans are pre-cooked and you don't need to soak them overnight like the dry variant; this considerably reduces the time needed to prepare them and, consequently, all of this has a positive effect also in terms of energy consumption. (Read also: Lupins: properties, calories, uses and contraindications)
Contraindications of canned beans
Canned legumes have a important nutrient profile and they are generally safe; although a 2020 study found that some canned foods contained environmental contaminants. However, this study focused mainly on canned meat and fish, and there are few references to legumes.
It is important to note that these results come from only one study, and more research is needed. Here are the main contraindications.
Canned beans may contain nitrates and nitrites
According to a search, nitrates and nitrites are preservatives used in canned foods and as food additives in processed meats; the reason? They help prevent the growth of mold and bacteria. They are also used as a fertilizer and are found naturally in fruits and vegetables.
High levels in canned legumes may indicate a contamination during agriculture and canning. Excessive consumption of nitrates and nitrites can interrupt the flow of blood and oxygen in the body.
However, these compounds are safe when taken in small doses; in fact, research has shown that they play an important role in production of nitric oxide in the body, helping to lower blood pressure, reduce blood clotting and the risk of heart disease.
Potential for heavy metal contamination
It has been shown that i heavy metals, like mercury, lead and cadmium, are toxic even at low concentrations. Although contaminated drinking water is the main source of exposure to heavy metals, one study of 2020 found too high levels of cadmium in canned beans.
Cadmium is found in soil, and is a common food contaminant which, as reported in a review, with long-term exposure it accumulates throughout the body and can impair the kidney function and bone health. (Read also: Canned chickpeas, found traces of glyphosate and pesticides. Cirio among the best brands in the test)
They contain salt
Salt (sodium) is an essential nutrient that helps the body regulate blood volume and blood pressure, but consuming too much salt can increase the risk of hypertension, kidney disease e ictus.
Le dietary guidelines 2020-2025 for Americans recommend limiting your daily sodium intake to 2.300 mg, which is equivalent to 1 teaspoon of salt. So, if you suffer from high blood pressure or heart disease, research has shown that you should further limit your intake to 1.500 mg (or 2/3 teaspoons) of salt per day.
How much salt do canned legumes contain? One can of canned beans can contain up to 25% of the recommended daily allowance of salt (570 mg).
Canned and glass legumes: which one to choose?
Canned legumes can be packaged in tin can or in glass, but what is the best option? Assuming that it would be better to choose organic ones to avoid traces of pesticides, glass is certainly the healthiest choice, because it is less subject to deterioration as well as allowing a visual check at the time of purchase. But above all, glass is the material that in contact with food releases the least substances and MOCA of all.
Obviously, before buying canned legumes, the advice is to always look there expiry date and packaging, which must not be earlier than 24 months before consumption. Also, it is advisable also check the packaging which must be intact, undamaged and without traces of rust and dents.
To conclude, canned beans and legumes, even if they have fewer vitamins and polyphenols due to cooking and the processing process, retain their nutritional richness and can be safely consumed if we have problems of time and practicality. Obviously fresh ones are preferred, but dried and canned beans can also be an excellent alternative, especially if chosen organic and in glass packaging. (READ also: Canned beans and chickpeas: find traces of glyphosate, bisphenol A and prohibited pesticides. Coop and Valfrutta the best)
- Follow your Telegram | Instagram | Facebook | TikTok | Youtube
On vegetable could it be interesting for you:
- Legumes: carbohydrates or proteins? How to combine them in a balanced meal according to the nutritionist
- Cicerchie, how to wash and cook them to minimize toxicity
- Legumes: carbohydrates or proteins? How to combine them in a balanced meal according to the nutritionist
- Red lentils flavored with glyphosate and pesticides. Residues found in almost half of the brands analyzed
- Legumes will save the world