How to accumulate the large amount of energy that the sun and the wind are able to produce? Storage is a current problem. The solution, however, could be low cost and once again provided by nature. In fact, Harvard is working on a new system of flow batteries capable of delivering energy without using expensive metals, but using plants. Rhubarb for example
He is about to end up run over, his mother saves him
How to do accumulate large amount of energy that the sun and the wind are able to produce? Storage is a current problem. The solution, however, could be low cost and once again provided by nature. In fact, Harvard is working on a new system of low-cost flow batteries capable of delivering energy without using expensive metals, but using plants. The rhubarb eg.
It is now clear that the next challenge in the renewables sector is to succeed in conserve "excess" energy, which the electricity grids are not yet able to manage given the enormous quantities.
One of the problems associated with solar and wind energy is that the flow of electricity produced by the sun and wind cannot by its nature be constant. This can cause problems if these systems are plugged into the power grid, which would have a hard time coping with sudden spikes. For this it would be useful to store the surplus of electricity.
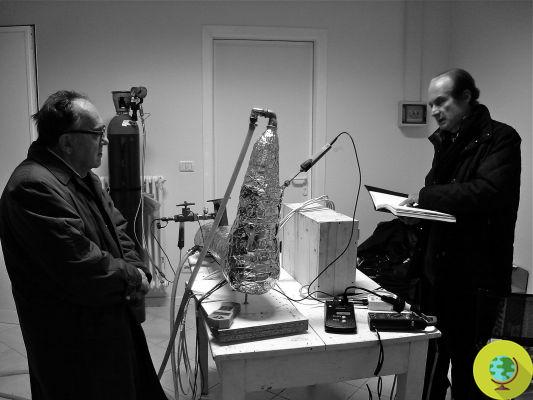
At Harvard University, chemists and engineers have been studying a new type of chemistry for over a year battery flow, based not on the vanadium used today (and very expensive) but on chinoni. What is it about? Quinone is part of a class of organic compounds abundantly present in nature, in plants such as rhubarb but also in the walnut tree and grapes. The raw material would therefore be much cheaper.
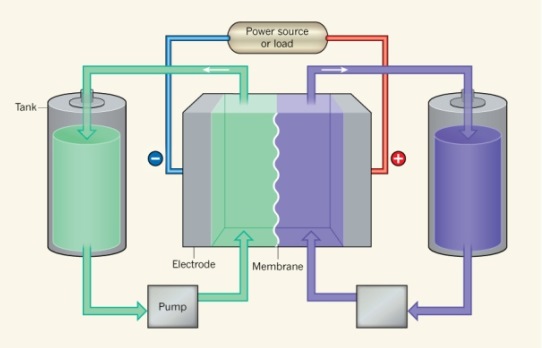
The negative electrode of the battery, the anode, is made up of a solution of chinoni diluted in sulfuric acid. The other end of the battery, the positive cathode, is made up of bromine. The anode reacts with the positively charged protons to form the high-energy hydroquinone. Quinone is inexpensive and does not require catalytic stress to react with protons to form hydroquinone.
Il model designed at Harvard it is only a laboratory experiment, at least for the moment, but it could be one of the solutions to store the large quantities of energy produced thanks to renewables.
Francesca Mancuso
ALSO READ:
- StreetScooter: from Germany the first low cost electric car in the world. It promises zero emissions at 5 thousand euros
- Wooden batteries to accumulate energy
- Batteries for electric cars from sulfur waste