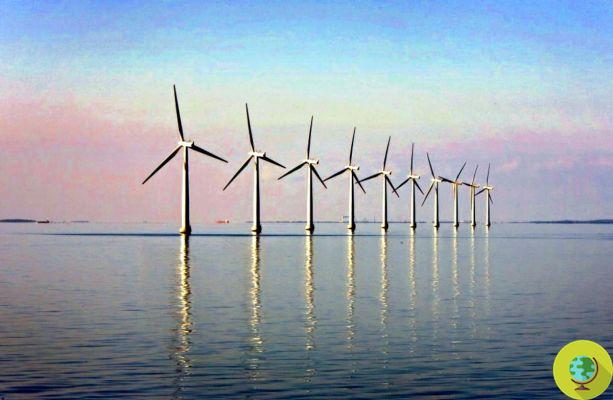
In the open ocean, and in particular in the Atlantic, wind power can produce up to 5 times the energy produced on earth. These are the results of the new (and promising) research by Anna Possner and Ken Caldeira, researchers at the Carnegie Institution for Science (Washington, USA)
He is about to end up run over, his mother saves him
In the open ocean, and particularly in the Atlantic, wind power can produce up to 5 times the energy produced on earth. These are the results of the new (and promising) work by Anna Possner and Ken Caldeira, researchers at the Carnegie Institution for Science (Washington, USA).
In the open ocean the wind it is on average stronger than that on earth, and therefore wind turbines could, at least in theory, intercept more than five times the energy produced on earth. Still only theory, because the methodology for converting everything into electricity is not yet known. However, an excellent step forward for themass use of renewables.
Most of the energy captured by large wind farms is generated in the atmosphere higher than where the turbines are located, and is then transported to the surface where it is captured and transformed into exploitable electricity. So it is now necessary to understand if the same thing can be done for the atmosphere above the ocean, or rather if the result is the same as predicted by the model.
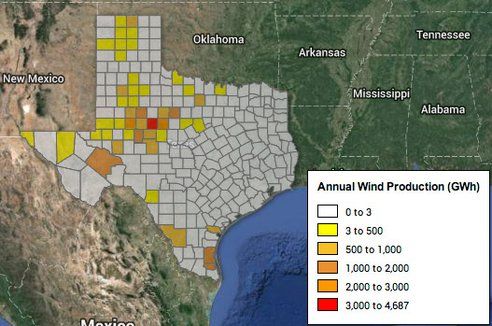
Possner and Caldeira's instruments compared the productivity of large wind farms in Kansas (USA) with that of enormous (but theoretical) wind farms in the open ocean and they found that in some areas, wind farms built on the ocean could generate at least three times the energy produced on earth.
Furthermore, in the North Atlantic, and particularly along the American coast, the occurrence of is (sadly) known cyclones which could be effectively used to bring energy from the upper atmosphere up to the height of the turbines.
However, this huge wind power is heavily dependent on the season. While in winter, wind farms in the North Atlantic could provide enough energy to meet all the needs of the population, in summer they would generate only the energy needed to meet the electricity demand of Europe or the United States.
Offshore wind power generation is in its own childhood marketing. The huge wind energy resources identified by the Possner and Caldeira study provide strong incentives to develop low-cost technologies that can transmit electricity to the ground where it can be used, but we would have to wait a long time before we have concrete applications.
Other promising sources of energy from the ocean:
-
SUBMARINE TURBINES THAT PRODUCE 10 TIMES MORE ENERGY FROM THE WAVES THAN A NUCLEAR POWER STATION
The work is published on Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Roberta de carolis
Photo: Terje Aase via EurekAlert