New study finds sleep deprivation or not getting enough sleep impacts hippocampus and memory
Don't store avocado like this: it's dangerousNot getting enough sleep can have serious repercussions on the hippocampus, a brain structure that, among other things, contributes to short and long-term memory. This is supported by new research from the University of Michigan.
That resting well and for a sufficient number of hours is fundamental for various aspects of our health is now known but new scientific research, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), now adds another important detail. (Read also: Insomnia: 10 Things That Happen to Your Body When You Don't Get Enough Sleep)
Sleep deprivation leads to increased activity of inhibitory neurons in the hippocampus, an area of the brain essential for orientation, as well as processing and storing new memories.
Consequently, not getting enough sleep (or even depriving yourself of sleep for example by spending a sleepless night to study or work) disrupts the processing and storage of new memories, in other words it has an extremely damaging effect on memory.
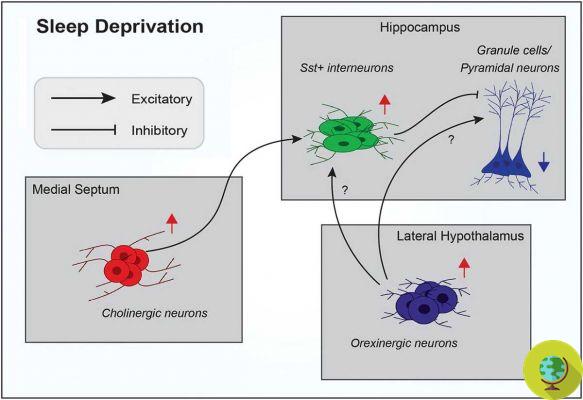
@Pnas
As Dr. Aton, an associate professor in the Department of Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology at the University of Michigan said:
As these neurons restrict activity in their vicinity, this physiological response makes it impossible to pick up normal neuronal activity in the hippocampal structure. I always tell my students that a sleepless night doesn't help them prepare for an exam.
These results, obtained on an animal model, however, if confirmed by further research could have important implications for learning strategies but not only.
Even in disorders such as Alzheimer's, where sleep difficulties are common, there may be a relationship between the physiological mechanism described in this study and memory loss. But, Professor Aton argues, there may also be a protective function of neurons, or an adaptive psychological reaction against stressful memories:
Sleep loss could sometimes be therapeutic. For example, using sleep deprivation after a traumatic event could be a way to prevent PTSD.
It really isn't the first time that sleep deprivation or insufficient night rest has been linked to poor memory. Already in 2014, scientists from the universities of Oxford, Cambridge, Harvard, Manchester and Surrey had pointed out in an interview that those who are content with sleeping 4 or 5 hours a night see a 15% reduction in the ability to memorize and learn easily. . (Read also: You sleep 2 hours less than 60 years ago, but what are the risks?)
- Follow your Telegram|Instagram |Facebook |TikTok |Youtube
Sources: University of Michigan / PNAS
Read also:
- Stages of sleep, what are they and how many hours of deep sleep does your body need to regenerate?
- If you wake up tired in the morning, you may have had little REM sleep. Tips and tricks to increase it and feel rejuvenated
- Going to bed early and sleeping well improves college performance. The MIT study
- Women need more sleep (at least 20 minutes), here's why