Neuroendocrine tumors, also referred to as TNE or NET (from the English Neuro-Endocrine Tumor), originate from endocrine cells and can affect organs as diverse as the intestine, pancreas, lungs, thyroid, thymus or adrenal glands
Fedez broke the silence and revealed that he had undergone an operation to remove a rare neuroendocrine tumor of the pancreas. Neuroendocrine neoplasms are very heterogeneous types of neoplasms, both in localization and in aggressiveness, but all originate from the cells of the neuroendocrine system. As for the tumor that can affect the pancreas, only a small percentage (5-10%) of pancreatic tumors originate from endocrine cells, while the majority is represented by tumors originating from duct cells. But, what's it about? And what are the symptoms that can suggest a neuroendocrine tumor of the pancreas?
Generally neuroendocrine tumors are a slow growth and not very aggressive, but there may be cases in which they manage to grow rapidly and severely.
Before explaining what the tumor that affected Fedez is, let's specify what the neuroendocrine system.
Index
Neuroendocrine system and neuroendocrine tumors
The neuroendocrine system is made up of cells that have the typical characteristics of endocrine cells, which produce hormones, and of nerve cells, hence "neuroendocrine". These cells are throughout the body and, depending on the organ in which they are found, perform specific functions, such as regulating the flow of air in the lungs or the rate of transit of food in the gastrointestinal tract or the release of digestive juices. in the intestine.
Neuroendocrine tumors, which in English are indicated by the acronym NET o NET (from the English Neuro-Endocrine Tumor), originate from these cells and can affect organs that are very different from each other such as the intestine, pancreas, lungs, thyroid, thymus or adrenal glands.
The neuroendocrine tumor of the pancreas
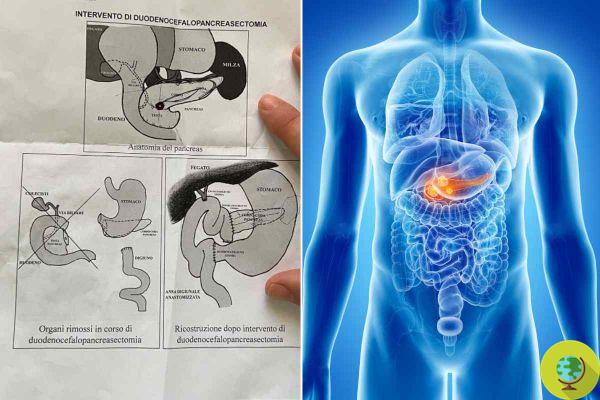
More correctly we speak of neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreatic islets to indicate that series of pathologies that can develop starting from the endocrine cells notes present in the pancreas. But they can also arise at the level of duodenum.
Only a small percentage, ranging from 5 to 10%) of pancreatic cancers originate from endocrine cells, while the vast majority are caused by duct cells.
Some pancreatic endocrine tumors are called "functional", as they are capable of producing an excess of hormonal substances responsible for more symptoms, and "non-functioning", which are the majority and which do not produce any substance.
The main types of cancer working I'm:
- isulinoma: produces an excess of insulin, a hormone that regulates blood glucose values
- gastrinoma: produces gastrin, a hormone that increases the production of acid by the stomach, thus causing ulcers to form and diarrhea
- glucagonoma: produces glucagon, a substance that causes diabetes and skin rash
- somatostatinoma: characterized by diabetes, gallbladder stones and difficulty digesting fatty foods
- VIPoma: causes an increased production of intestinal vasoactive peptide (VIP), a hormone that controls the secretion and absorption of water by the intestine, and is characterized by profuse diarrhea
It goes without saying that all of this often involves specific symptoms. Let's see which ones.
Symptoms of neuroendocrine tumors
Depending on the hormone produced by the tumor, various symptoms can occur; the main ones are:
- diabetes
- hypoglycemia
- cholelithiasis
- duodenal ulcers
- Diarrhea
In addition to the symptoms due to the production of hormones, others are instead linked to the effect of the tumor itself, especially present in the case of a non-functioning tumor.
The main ones are:
- pain
- jaundice
- slimming
- vomiting
How a neuroendocrine tumor is discovered
If sometimes the suspicion arises with the above symptoms, other times it is discovered by chance, through diagnostic tests aimed at something else. To have a certain diagnosis, we resort to:
- three-phase computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdomen
- ecoendoscopia
- PET-CT (Positron Emission Tomography with CT fusion), to date one of the most important investigations for the diagnosis and re-establishment of neuroendocrine tumors
- receptor scintigraphy
- biopsy: this is a sample of tumor tissue, which is then examined under a microscope. It is essential to understand if it is a poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma
- genetic analysis for MEN1 syndrome
How to cure
- surgical removal of the tumor, which is the first choice and most effective treatment
- biotherapies, monthly injections of a synthetic hormone analogue of somatostatin (octreotide or lanreotide). This therapy can improve symptoms (in functioning tumors) and slow tumor growth
- chemotherapy
- radiometabolic or radio-receptor therapy
Follow your Telegram | Instagram | Facebook | TikTok | Youtube
Sources: AIRC / Humanitas
Read also:
- Pancreatic cancer: symptoms, risk factors, survival rate
- Pancreatic cancer: little known but growing killer, world day is born