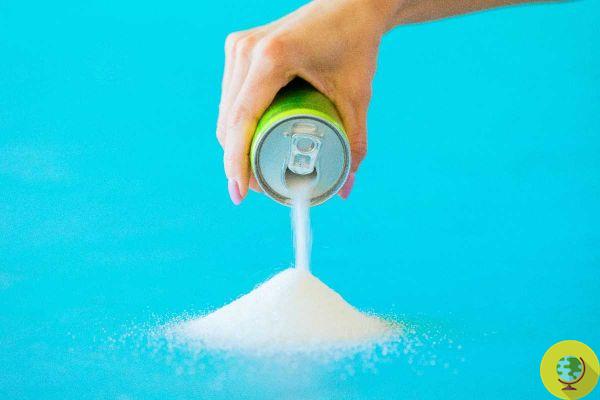
New research has shown how excessive consumption of sugary drinks in adolescence can increase the risk of bowel cancer
Don't store avocado like this: it's dangerousNew research has shown how excessive consumption of sugary drinks in adolescence can increase the risk of bowel cancer
Cancer can strike anyone at any time, but it is now certain that some choices on lifestyle can increase the risk. A recent study demonstrated how the Consumption of sugary drinks can double the risk of bowel cancer. Cancer cells are difficult to treat because they divide and multiply in the body very quickly, often spreading to other areas before being detected; however, research suggests that certain lifestyle choices may partly determine the risk of developing the disease. (Read also: An initial correlation has been discovered between children's consumption of sugary drinks and their academic performance)
Drinking two or more sugary drinks a day in adulthood has been linked to a doubling of bowel cancer risk before age 50, at least in women. According to the research team, each daily serving is associated with a 16% higher risk, rising to 32% per daily serving during adolescence.
The study revealed that sugary drinks, such as soft drinks, fruit-flavored drinks, sports and energy drinks, are the main source (39%) of added sugars in diets, and 12% of the population drinks more than three servings each. day. To probe the link between sugary drinks and bowel cancer risk, the researchers drew on information provided by 95.464 participants in the Nurses' Health Study II, an ongoing monitoring study of 116.429 nurses between the ages of 25 and 42.
The women reported what they ate and drank, using validated questionnaires on food frequency every 4 years, starting in 1991; and 41.272 of them reported what and how much they drank during their adolescence (13-18) in 1998. Information was also provided on potentially influencing factors, including family history of bowel cancer, lifestyle, regular use of aspirin or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and vitamin supplements.
In 1989, participants were asked to remember their health, weight (BMI) and lifestyle during adolescence. During 24 years of monitoring, 109 women developed bowel cancer before age 50. A higher intake of sugary drinks in adulthood was associated with a higher risk of the disease, after taking into account potentially influencing risk factors. Compared to those who drank less than one serving per week, women who drank up or more each day were more than twice as likely to develop bowel cancer.
Replacing sugary drinks with artificially sweetened drinks, coffee or semi-skimmed or whole milk, has been associated with a 17% to 36% lower risk of being diagnosed with bowel cancer before age 50. It is important to note that this is an observational study and as such cannot establish a cause, only a correlation.
In addition, according to the researchers, given that most of the participants were white women, the findings may not apply to men or other ethnic groups. However, they pointed out that there are some biologically plausible explanations for their findings: the sugary drinks suppress the sense of satiety, leading to excessive calorie intake and weight gain.
These drinks also cause a rapid increase in blood sugar and insulin secretion which, in the long term, can induce insulin resistance, inflammation, obesity e 2 type diabetes. Emerging evidence also suggests that fructose may impair gut barrier function and increase gut permeability, which could promote the development of cancer.
Hence, reducing their intake or replacing these drinks with healthier ones among adolescents and young adults may serve as a potential viable strategy to decrease the risk of bowel cancer before age 50.
I bowel cancer symptoms They include:
- a persistent change in bowel habit, i.e. going to the bathroom more often, with looser, more fluid stools and sometimes belly (abdominal) pain
- blood in the stool without other symptoms such as hemorrhoids
- abdominal pain, discomfort or bloating always caused by eating, sometimes resulting in a reduction in the amount of food consumed and weight loss.
Follow us on Telegram | Instagram | Facebook | TikTok | Youtube
Photos: BMJ
Could it be interesting for you:
- If you are over 50 this is the most dangerous food: it quadruples the risk of cancer "almost like smoking"
- A very popular supplement could increase the risk of lung cancer when taken in high doses
- Prostate cancer: Too many selenium and vitamin E supplements would increase the risk
- The main causes of breast cancer you should know about
- Are you going to the bathroom in the middle of the night? It could be a symptom of this type of cancer
- Prostate Cancer: Exposure to PFAS and a high-fat diet increase the risk of cancer