Why mulch, how to do it correctly and which materials are best suited for our vegetable gardens and gardens
Why mulch, how to do it correctly and which materials are best suited for our vegetable gardens and gardens
Not everyone knows the meaning of the term "mulch" but surely everyone has seen some examples sooner or later in gardens, nurseries or vegetable gardens. This term indicates any material used as ground cover. (Do you know the ingenious newspaper trick to stop weeds from growing?)
Index
What is mulch used for?
Mulch serves several purposes, let's see the main ones:
- retains moisture in the soil;
- prevents the growth of weeds;
- keeps the earth cool;
- protects from frosts;
- has an aesthetic function.
If distributed correctly, mulch significantly reduces the time spent on garden maintenance, because you no longer have to worry about weeding, and you can water less, as it retains a lot of moisture, allowing significant water savings. It also promotes the development of healthier soil, hindering pest infestations. Here you will have healthier flowers, vegetables and fruits.
However, it is necessary to make two general distinctions on the types of mulch that can be used: organic mulches and inorganic or synthetic ones.
Organic mulch
Organic mulch is that material that derives from matter that was once alive. This will tend to decompose, releasing valuable nutrient material to the soil. The more woody and dry it is, the longer it will take to decompose and the less nutrients it will donate to the soil. When choosing this type of material it is very important to make a quality choice, since we will have to avoid that it contains weed seeds or worse that it derives from material previously treated with chemicals that will then poison our soil. Let's see the main types of organic mulch.
The bark

Chopped bark or wood chips are an ideal choice for mulching around trees, shrubs or flower beds. In all the places where we would have a perennial crop, and which we will not have to replant the following year. This is because digging the new hole would end up inside all the pieces of wood, mixing with the ground and risking to cause rot at the roots.
Grass cut
A good habit would be not to completely throw away the grass we cut. This can be an excellent mulch for all those areas of the garden that are less traveled and frequented and that have a tendency to develop weeds. Another reason why it would be better to use it at the margins is because when it decomposes it gives off an unpleasant odor and to be slimy given the high water content. However, it is rich in nitrogen so using a little bit of it in the garden is a great way to naturally fertilize the soil.
The newspaper clippings
Increasingly in vogue, this method makes it possible to recycle newspaper paper as more and more natural, organic dyes are used. The sheets have a great capacity to retain moisture and for this reason, for years, nurserymen have used them to wrap and ship plants. They are also effective in suppressing weed growth and keeping the soil temperature more constant. They are unpleasant to see so often double mulching is used. A layer of newspaper clippings is spread and on top a second layer of mulch that is aesthetically more beautiful and tidy.
Dry leaves
Without a doubt the mulch par excellence, the one that mother nature prefers. It can be used anywhere, gardeners simply do not use it for an aesthetic reason, even if things are changing since the taste that is gaining momentum is a return to the rustic, to the natural. Furthermore, dry leaves are the ideal habitat for earthworms, essential for nourishing and enriching the earth.
Straw and hay
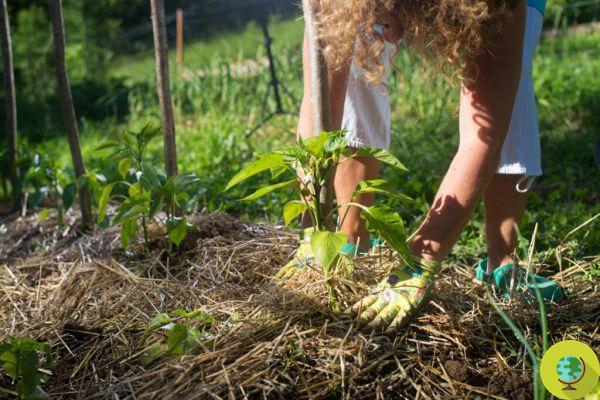

Particularly suitable for cultivating the vegetable garden. They effectively retain moisture on the ground, protecting leaves and grassy plants in general from water stagnation and therefore from rot. Straw also has a longer decomposition time so it will last for the entire growing season. Like dry leaves, straw and hay are also the ideal habitat for spiders and insects that are very useful to counteract the infestation of parasites harmful to plants.
The compost
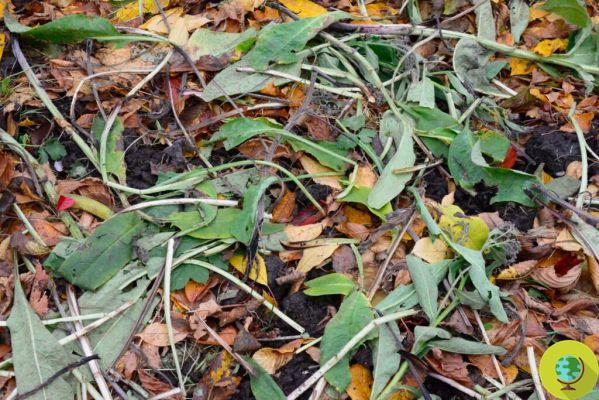

Well even compost can be an excellent mulch. Provides great enrichment to the soil. A thin layer, in turn, covered with dry leaves or another organic cover is enough. As you can imagine, it is particularly suitable for the vegetable garden.
Inorganic or synthetic mulch
With this definition we mean all plastic materials, inorganic in fact, geotextiles or stones with which land coverings are made. Usually, given the unpleasant appearance, they are used in combination with organic mulches. However, they do not provide any contribution or enrichment to the land, on the contrary they can contribute to their pollution.
Like organic ones, they are suitable for retaining moisture and blocking weeds.
The plastic
It retains solar heat well allowing the ground below to have up to three degrees more temperature. It prevents the growth of weeds but must be drilled far enough to not create mold. There are plastics with infrared transmission, since they are transparent, which have higher costs but which allow a higher yield. However, plastic does not decompose.
Geotextiles or non-woven fabrics (TNT)
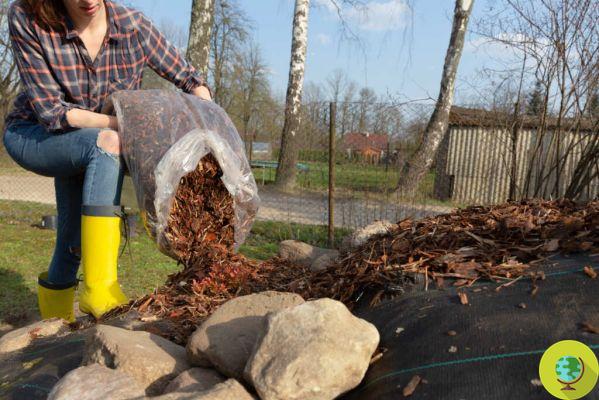

Unlike plastic, these fabrics let air and light through, so the ground below can breathe. They also decompose especially when exposed to light. Therefore to make them last longer it is advisable to cover them with bark, for example, even more pleasant to see.
Stone or gravel
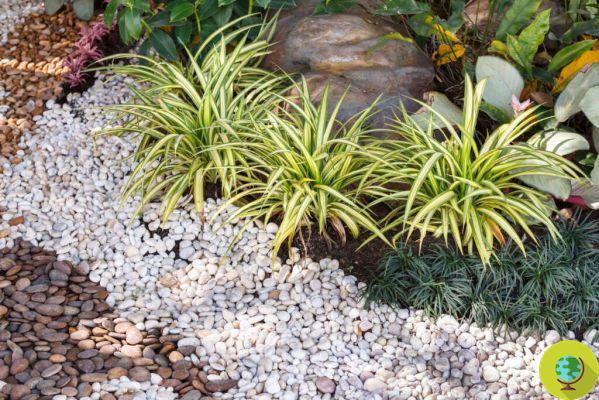

They retain soil moisture well and effectively prevent weed growth. They do not decompose so they are durable and it is recommended to use them in all those areas where there will be perennial crops such as trees, hedges and shrubs. Since it is complicated to remove them to create new holes to plant again.
How to mulch properly
A few basic rules to optimize mulching work:
- spread a 10 cm layer to be sure to effectively prevent weed growth. A few cm less may be enough only if the point where we spread it is shaded therefore the growth of plants and grass will be slow and less;
- use the double mulch technique especially if we use inorganic mulches;
- in spring remove the mulch from bulbs and perennials to allow faster growth and flowering;
- always keep a short distance between the mulch and the herbaceous stems of plants and woody shrubs to avoid contact rot. Damage that would also allow rodents (mice and voles) to nest, damaging the plants.
Follow us on Telegram | Instagram | Facebook | TikTok | Youtube
You may also be interested in mulching:
- Do you know the ingenious newspaper trick to stop weeds from growing?
- Weed control in organic farming: mulching
- What to do if you find mold in strawberries and how to prevent it
- How to grow tomatoes in pots, in the vegetable garden and upside down: the mini-guide
- 10 ways to get rid of weeds (without using Roundup)