The ketogenic diet is basically a low carb diet, but it's not for everyone. Here's how it works. A low-carb diet that tends to drastically reduce carbohydrates. How ketogenic diets works, the goal of which is to bring the body back to a particular metabolic state is in many ways similar to that obtained by fasting
Don't store avocado like this: it's dangerous
A keto or ketogenic diet it is a low carbohydrate diet, according to which your body transforms itself into a real "fat burning machine". It might have the ability to lose weight, but what does a ketogenic diet actually consist of? And does it really work?
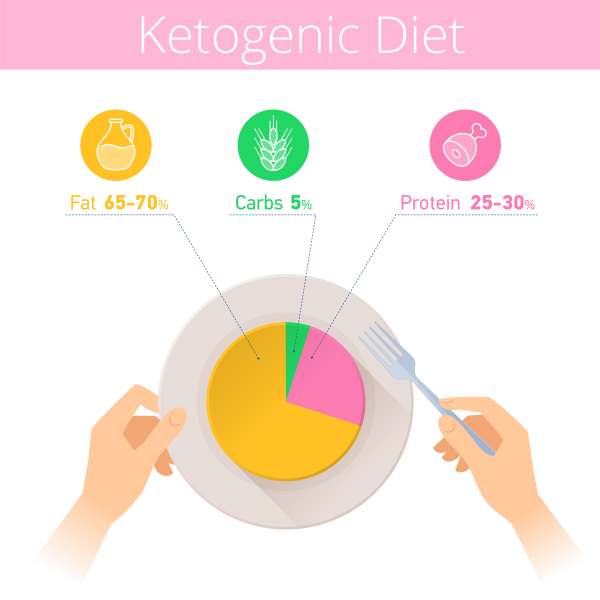
More than a "diet", those who support its virtues tend to define the ketogenic diet a "nutritional strategy"Which is based on the reduction of carbohydrates associated with an increase in the proportion of fat in the diet (generally in the measure of 75% fat and 25% of carbohydrates and proteins) and which induces the body to a defined state of"ketosis". With it, that is, the organism would be "forced" to independently produce glucose necessary for survival and to increase the energy consumption of fats contained in adipose tissue.
The ketogenic diet, therefore, would exploit the body's ability to convert fat into energy. Its peculiarity is also the use of supplements in order not to make the body lack anything especially in the initial period of the diet.
Index
What does "ketogenic" mean
The name "ketogenic" derives from the fact that this diet causes the body to produce small fuel molecules called "ketones", an alternative fuel for the body used when glucose is scarce. Our body, in fact, has two options to use as metabolic fuel: either the glucose or ketones (the alternative fuel). When carbohydrates are not available or sufficient to produce glucose (in the case of a fast, for example), the body produces ketones from fat such as alternative energy source.
Hence, ketones are produced if you ingest very few carbohydrates (which are quickly broken down into blood sugar) and only moderate amounts of protein (excess protein can also be converted into blood sugar).
Ketones are produced in the liver, from fat, and as "fuel," they too are used throughout the body, including the brain.
When the body produces ketones, it is said to be "in ketosis". The fastest way to get there is the complete fasting (so it can be said that the ketogenic diet, by limiting carbohydrates, mimics the metabolic state of fasting), but obviously it is impossible to follow it forever.
Read also: Fasting mimicking diet, does it really work? The results of the research
What is the ketogenic diet and how does it work

As we have seen, the ketogenic diet is an eating style that induces the body to form ketone bodies by itself, i.e. those acid substances from which it takes its name, such as beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetone and acetacetic acid. The production of ketone bodies occurs when they are taken very few sugars: in this case the organism and the brain begin to use ketone bodies as a source of energy.
In other words, ketone bodies reach a higher level than in a normal condition and their excess, responsible among other things for lowering blood pH, is called ketosis. The presence of ketone bodies in the blood exerts various effects on the body, first of all a rapid weight loss.
In the medical field, the ketogenic diet is used in cases of epilepsy, because it has been observed that it would be able to sedate the crises, while the application of the diet to other pathologies is being studied.
Lately, however, there is a tendency to "use" this diet simply for lose weight, underestimating that it is still a regimen that must be followed by a specialized doctor and that often needs to be accompanied by some supplements.
The ketogenic diet as a non-drug medical therapy
Since ketone bodies can be used by the brain as an alternative fuel to glucose, they have been the basis of the therapy of choice for decades now. GLUT1 deficiency syndrome in which the synthesis of the glucose transporter to the brain is genetically deficient (these are diseases in which there is an alteration in the utilization of carbohydrates and therefore a deficit in the availability of energy in the brain).
But the ketogenic diet was originally developed at the beginning of the last century to treat drug-resistant forms of epilepsy in children. The condition of ketosis or ketoacidosis would in fact be able to reduce the manifestations and severity of convulsive seizures.
Ketogenic diet, what to eat and sample menu
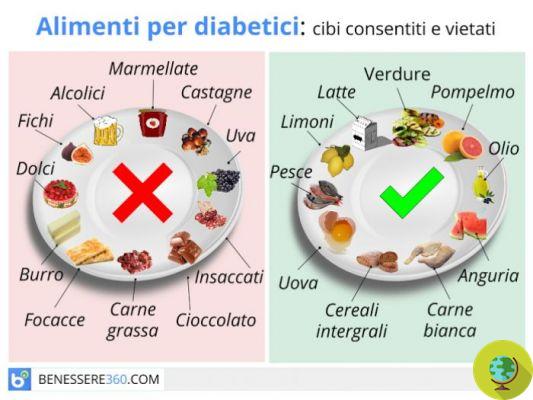
It is clear, therefore, that in order to reach the state of ketosis it is necessary eat foods that do not contain carbohydrates, limit those that bring few and avoid foods that are rich in it.
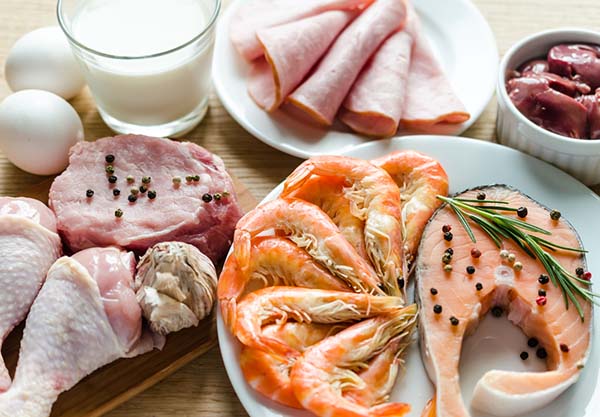
The foods that can be eaten on a ketogenic regime are:
- meat, fishery products
- eggs
- cheese
- seasoning fats and oils
- vegetables
To avoid:
- cereals, potatoes and derivatives
- vegetable
- soft drinks, sweets
Example menu
This is a one week general ketogenic menu that can be modified to suit individual dietary needs (Source):
Monday:
Breakfast: two fried eggs with stir-fried vegetables
Lunch: A herb burger topped with cheese, mushrooms and avocado with vegetables
Dinner: Pork chops with green beans sautéed in coconut oil
Tuesday:
Breakfast: omelette with mushrooms
Lunch: Tuna salad with celery and tomato and vegetables
Dinner: Roast chicken with cream sauce and sauteed broccoli
Friday:
Breakfast: pepper stuffed with cheese and eggs
Lunch: rocket salad with hard-boiled eggs, turkey, avocado and gorgonzola
Dinner: Grilled salmon with spinach sauteed in coconut oil
Thursday:
Breakfast: low-fat yogurt
Lunch: Steak with cauliflower rice, cheese, herbs, avocado and salsa
Dinner: Steak with cheese broccoli
Friday:
Breakfast: Baked avocado
Lunch: Caesar salad with chicken
Dinner: pork chops with vegetables
Saturday:
Breakfast: Toast with cauliflower topped with cheese and avocado
Lunch: salmon burger
Dinner: meatballs served with courgette spaghetti and parmesan
Sunday:
Breakfast: Coconut milk chia pudding topped with coconut and walnuts
Lunch: salad made with vegetables, hard-boiled eggs, avocado, cheese and turkey
Dinner: Chicken with coconut and curry
Ketogenic diet, why it should be avoided and who cannot follow it
Like many similar diets, ketogenic is essentially one unbalanced diet that tends to limit the intake of some very important nutrients. It goes without saying, therefore, that this diet can lead to many disadvantages, most of which depend on the levels of ketone bodies present in the blood.
Beyond the syndrome called "keto flu", That is a condition of generalized discomfort caused by the metabolic imbalance still not fully compensated by the body, the Department of Public Health of the University of Pavia has indicated in a very exhaustive manner the various short and long-term damages that can derive from a similar eating style. Even when used as a "therapy", it can have some side effects.
Main short-term complications:
- nausea and vomit
- Diarrhea
- refusal of food, loss of appetite
- drowsiness
- hypoglycemia Dis
- didratation
- acidosis (increase in acidic substances in the blood)
Main long-term complications:
- constipation
- hyperuricemia (increased uric acid in the blood); Hypocalcemia (decrease in the level of calcium in the blood); Hypoproteinemia (decrease in the amount of protein in the blood)
- kidney stones (formation of stones in the urinary tract)
- acidosis (increase in acidic substances in the blood)
- growth retardation
Then there are those who should not even remotely think of following a ketogenic diet and these are those who:
- they take diabetes medications, such as insulin
- are taking medications for hypertension
- breastfeed
Read also: Carbohydrates: which ones to choose based on the glycemic index?
You may also be interested in the following diets:
- DIET OF THE GLYCEMIC INDEX
- DIET FOR DIABETICS
- ICE CREAM DIET
- DIET OF LEMON AND GRAPEFRUIT
- HYPOCALORIC DIET
- SLIMMING DIET
- VEGETARIAN DIET
- DIGIUM MIME DIET
- ZONE DIET
- DIET DISSOCATED
- PROTEIN DIET
- DIET OF MINESTRONE
- SLIMMING WITH GINGER