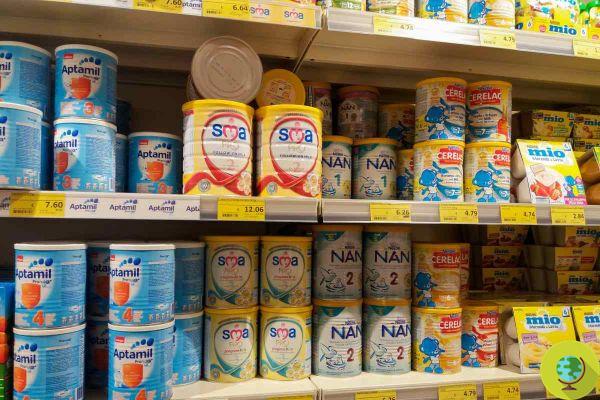
Brussels has further lowered the maximum tolerable levels of lead and cadmium in food.
Don't store avocado like this: it's dangerousAs part of the European Cancer Plan, Brussels has further lowered tolerable maximum levels of lead and cadmium in food. Objective: to reduce the exposure of the population to these metals dangerous for health
A few days ago two new European regulations came into force which lower the maximum levels of metals in a series of products. These are measures that aim to further reduce the presence of carcinogenic contaminants in food and make healthy food more accessible.
In fact, on 9 and 10 August, with Regulations (EU) 2021/1317 and 2021/1323, the European Commission amended Regulation (EC) 1881/2006 as regards the maximum levels of lead and cadmium in some food products. Heavy metals are compounds that can be found in the environment and derive from both natural and industrial sources and cadmium and lead, included among these contaminants, occur in food as residues.
Read also: Arsenic, cadmium and lead in fruit juices. The brands promoted and rejected in the USA
Strengthening the legislation was essential given the conclusions of the recent French study which underlined that the entire population is exposed to these metals and that the situation has worsened since 2006 for cadmium.
Already in 2009 the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) noted that:
the average [cadmium] exposure of European adults approaches or slightly exceeds the tolerable weekly dose and that the exposure of subgroups such as vegetarians, children, smokers and people living in highly contaminated areas can reach about double that dose.
The health effects of lead and cadmium
Cadmium is recognized as probable carcinogen, possible mutagen and toxic for reproduction by public health agencies. It can also lead to kidney damage and bone fragility.
The main sources of exposure are:
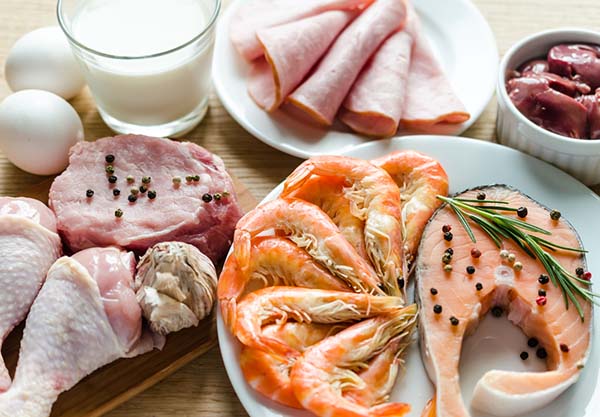
- molluscs and crustaceans
- breakfast cereals (for children)
- bread and bread products
- potatoes and derivatives
- tobacco
Lead is a neurotoxic, with harmful effects on the central nervous system, particularly in children (with risk of mental developmental delay). There is also cardiovascular and kidney damage.
The main sources of exposure:
- crustaceans and molluscs
- bread
- animal products
- tap water
- alcohol
- tobacco
The new European regulations
In the light of those developments and the most recent occurrence data, dietary exposure to lead in food within the Union should be reduced by lowering current maximum levels or by setting additional maximum levels for food for which it is reasonably possible. obtain lower lead levels, the regulation states.
Maximum lead levels have been lowered for:
- infant formulas, follow-on formulas marketed in powder form
- cereal based foods and other foods for infants and young children
- powdered foods for special medical purposes for infants and young children
- liquid beverages for infants and young children, including fruit juices, or to be reconstituted
- offal of cattle and sheep, pigs and poultry, with different limits based on the species of origin
- various wine products
while yes establishes the maximum limit of lead for:
- formulas for children
- root and tuber vegetables (excluding salsify, fresh ginger and fresh turmeric), bulb vegetables, flowering cabbage, head cabbage, kohlrabi, legumes and stem vegetables
- wild mushrooms
- fresh turmeric, fresh ginger
- vini liquorosic
- spices,
- sale
As for the cadmium, innew maximum levels are established for:
- some types of fruit from trees and dried fruit
- root and tuber vegetables, bulb vegetables, fruit vegetables, cabbage, leafy vegetables and aromatic herbs, legumes, stem vegetables
- mushrooms
- dried legumes and proteins derived from dried legumes
- oil seeds
- cereals
- powdered foods for special medical purposes for infants and young children
- formulas for infants and children
- beverages intended for infants and young children labeled and sold as such
- sale
What remains unchanged?
I maximum limits of lead and cadmium allowed will remain unchanged for:
- specific products based on cocoa and chocolate
- products of animal origin: meat and fish
- infant and follow-on formulas (only the terms "powdered infant formulas" and "liquid infant formulas" are replaced by "marketed as powder" and "marketed as liquid" respectively)
- food supplements excluding food supplements consisting exclusively or mainly of dried seaweed, products derived from dried seaweed or bivalve molluscs
Follow us on Telegram | Instagram | Facebook | TikTok | Youtube
Source: European Commission
Read also:
- How to cleanse yourself of heavy metals: 10 foods and natural remedies
- Sushi, too much cadmium in nori and wakame. The alarm of the French agency
- Spirulina and seaweed supplements: contain too many heavy metals
- These common food additives can be harmful to children, pediatricians say
- The new WHO guide that sheds light on baby food between 6 and 36 months