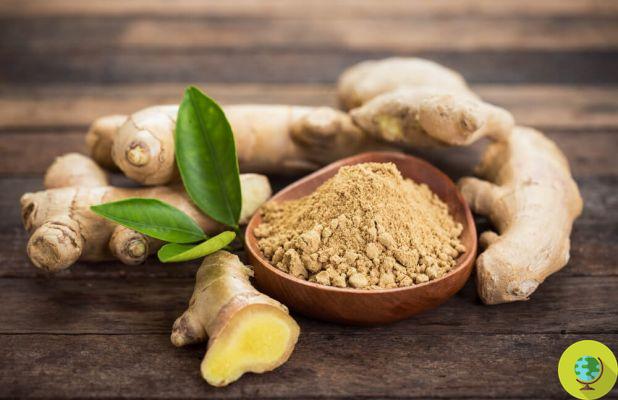
Ginger is a tasty spice and a drug with numerous benefits but when consumed in excessive quantities or by people with certain ailments it can give some unpleasant side effects.
Ginger is a tasty spice and a drug with numerous benefits but when consumed in excessive quantities or by people with certain ailments it can give some unpleasant side effects.
Ginger is a particularly popular spice for her flavoring and beneficial properties. Added fresh or powdered to dishes, consumed in infusions and drinks, eaten candied or in the form of candies, this rhizome is able to surprise for its its strong and spicy taste and for its antiemetic properties.
As with any food or substance, however, ginger can also have side effects if consumed in excessive quantities.
As Paracelsus said, in fact, “it is the dose that makes the poison”, therefore better never to abuse any food or substance, since even if natural, excessive quantities can cause problems rather than benefits. Also better not to take it in case of certain disorders or pathologies.
5 side effects of ginger
- Due to the cholagogue action of ginger, i.e. the ability to stimulate the production of bile by the gallbladder, the intake of this rhizome is not recommended in case of gallbladder stones.
- Ginger contains gingerols and shogaols, compounds that can cause mutagenicity. Although there is no proof in the literature that justifies one contraindication in pregnancy, the German Commission E advises against taking ginger in this circumstance.
- Although no cases of drug interactions, since ginger has an antithrombotic effect, the use of this drug should be avoided in patients undergoing treatment with anticoagulants.
- Ginger stimulates gastric secretions: at the recommended dosages it has a gastroprotective action but excessive consumption could cause stomach ache and worsen the symptoms of those suffering from gastro esophageal reflux.
- In people particularly sensitive to the spicy taste or allergic subjects, ginger can cause irritation, burning and itching of the mouth. In some cases, ginger can also cause tingling and swelling of the oral mucosa.
As far as phytotherapeutic preparations are concerned, generally the daily dosage of ginger it is equal to 12-13 mg per kilo of body weight, divided into two doses, preferably on an empty stomach; much higher dosages of ginger are required for side effects to occur.
You may also be interested in ginger:
- Ginger and Lemon herbal tea: benefits, when to drink it and how to prepare it
- Ginger and garlic: how to prepare the infusion and pasta to use in the kitchen
- Gingerbread cookies glazed with water: the recipe for gingerbread without butter
- Ginger and moringa: why use them together and how to prepare the herbal tea
- If you find yourself in any of these conditions, avoid ginger, it is bad for your health
- Ginger detox bath: all the benefits and how to prepare it
- 10 recipes to enrich with… a touch of ginger
- Ginger: origins, legends and magical properties attributed to the root
Tatiana Maselli