Here are the symptoms of Cytomegalovirus and why it can be dangerous in particular conditions such as pregnancy.
Don't store avocado like this: it's dangerousIl Cytomegalovirus it's a virus very common belonging to the herpes virus family (such as cold sores, genital herpes and chicken pox virus). Its name refers to the fact that it is capable of causing a considerable increase in the size of the cells it affects. But what are the symptoms of cytomegalovirus? And why it can be dangerous in particular conditions such as the pregnancy?
It is a virus that can infect anyone and it is so widespread that it reaches 90-100% of the population of underdeveloped countries, while in Western countries 60-80% of adults have anti-Cytomegalovirus antibodies, with 40% of children already infected.
Once you have contracted Cytomegalovirus, the infection remains latent and, as in the case of other herpes viruses, it can reactivate in situations of weakening of the immune system.
Index
What is Cytomegalovirus
Cytomegalovirus (or also CMV, cytomegalovirus or human herpes virus 5) is a infectious agent spread all over the world which is part of the herpes virus family, which includes microorganisms responsible for common diseases such as:
- chickenpox
- cold sores
- genital herpes
- infectious mononucleosis
- the shingles
READ also: HERPES: TYPES, SYMPTOMS AND NATURAL REMEDIES
Who has already contracted the CMV once it does not remain completely immune from it, on the contrary, he has every possibility of contracting a reinfection. Based on this, the infection is distinguished in primary o recurring, which in turn is distinct into reactivation (from viral strain already present in the subject) e reinfection (from a viral strain other than the one that had previously infected the organism).
The virus mostly contracts through saliva, blood, urine and sexual intercourse. Infection is rarely transmitted indirectly, with the use of objects such as a glass, a toothbrush or, as for children, a toy or pacifier.
One of the fundamental aspects related to the Cmv is represented by the congenital infections: an infection contracted during pregnancy and transmitted to the fetus can in fact cause permanent and serious damage to the unborn child.
READ also: MOUTH HANDS FEET: CAUSES, SYMPTOMS AND HOW TO RECOGNIZE THE DISEASE (PHOTO)
Cytomegalovirus symptoms
In most cases one Cytomegalovirus infection is completely asymptomatic or has symptoms almost imperceptible.
Most healthy individuals who contract the disease essentially have no symptoms and are unaware of the infection. some people develop a mild form of the disease with symptoms typical of a common flu (fever, sore throat, fatigue and swollen lymph nodes). In immunosuppressed people, that is, with reduced immune defenses, the virus can be the cause of serious diseases, such as pneumonia, hepatitis or encephalitis.
In summary, what is manifest or in immunosuppressed subjects, CMV can have symptoms as:
- fever and chills
- general malaise
- sore throat
- fatigue and muscle aches
- enlarged lymph nodes
Sometimes, they can show up more severe signs such as inflammation of the lungs, eyes, liver, spleen or digestive tract.
READ also: MONONUCLEOSIS: SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT OF THE KISSING DISEASE
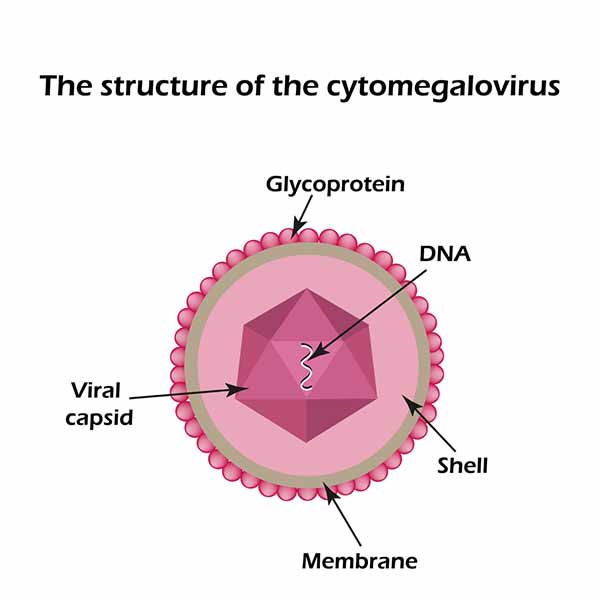
Congenital Cytomegalovirus Symptoms
The phenomenon of congenital cytomegalovirus is different: in this case, i symptoms typical of children infected with the virus before birth (which in turn can spread the virus even for three years after birth) can be distinguished in temporary e permanent.
Temporary symptoms in children infected with CMV include:
- petechiae, red patches on the skin corresponding to small hemorrhages
- convulsions
- jaundice
- small size at birth
- liver problems
- problems with the spleen
- lung problems
While more permanent than symptoms are real disabilities, as:
- blindness
- deafness
- convulsions
- microcephaly
- movement coordination problems
- mental delay
In all cases it is symptoms that can appear long after birth, for which doctors generally recommend that all children born with cytomegalovirus infection be periodically checked.
Citomegalovirus cause
There are many factors that can increase the risk of developing Cytomegalovirus infection, including attendance of kindergartens and schools, Tight contact with an infected person or even a weakening of the immune system. This is why it is particularly easy to become infected during childhood (environmental promiscuity) and during puberty, with the first sexual intercourse.
The contagion, in fact, takes place only through direct person-to-person contact because of the secretions oral-pharyngeal, vaginal and spermatic, but also through breast milk or contact with tears, urine or feces of an infected person. Nor are the transfusions of infected blood or blood products, and bone marrow or organ transplants.
The transmission, then, from mother to fetus during the nine months of pregnancy is one of the key points of concern.
Ultimately, the causes that lead to the spread of a CMV infection are:
contact from subject to subject with consequent transmission of body fluids
mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy or breastfeeding
transfusions or transplants of infected organs
Congenital Cmv infections, because Cytomegalovirus is dangerous in pregnancy
Pregnant women are among those "immunosuppressed" subjects particularly at risk of infection. But the danger has not escaped even for those who have already contracted the virus before pregnancy, because, as we said, it is reactivation of latent CMV or reinfection with a new strain around the corner.
Infection a vertical transmission from mother to fetus - which is not related to a certain gestational period - it is said primary when a previously seronegative woman acquires it for the first time during pregnancy; secondary when, in a woman who had already contracted the infection, it occurs by reactivation of the latent virus or by reinfection from a new strain.
According to data from the Istituto Superiore di Sanità, the risk of transmission to the fetus ranges from 30 to 40% in the primary form and is between 0,5 and 2% in the secondary form. 85-90% of infants with congenital infection have no symptoms, but about 10% of asymptomatic infants have late sequelae, usually hearing defects.
Il About 10-15% of newborns and instead symptomatic, with symptoms that - as we have seen previously - can be temporary or permanent.

as to diagnosis, to understand if there has been vertical transmission, they are necessary It is invasive such as amniocentesis or fetal blood analysis, while to detect congenital cytomegalovirus infection in the newborn, blood, urine and saliva tests will be enough during the first three weeks of life.
Like all other categories most vulnerable to the disease, pregnant women must also follow careful personal hygiene.
On the pregnancy you may also be interested in:
PREGNANCY: NEW WHO GUIDELINES. THE RECOMMENDED VISITS UP TO 8
10 SUPER CIBI PER GRAVIDANCE
FOLIC ACID: BENEFITS AND SIDE EFFECTS
How to avoid infection:
It is always a good idea to always:
- washing hands with hot water and soap before eating and cooking, after coming into contact with urine or feces of children if you already have them, after going to the bathroom and after any kind of contact with body fluids
- avoid exchanging cutlery or other utensils during meals, especially if you already have small children
- clean the surfaces contaminated with body fluids carefully and with a pair of gloves
Germana Carillo