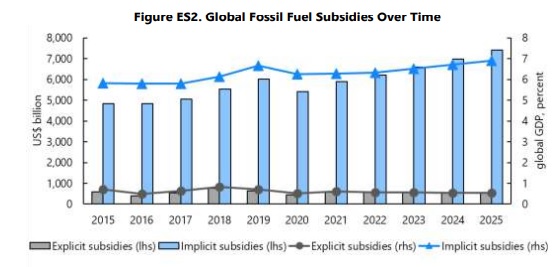
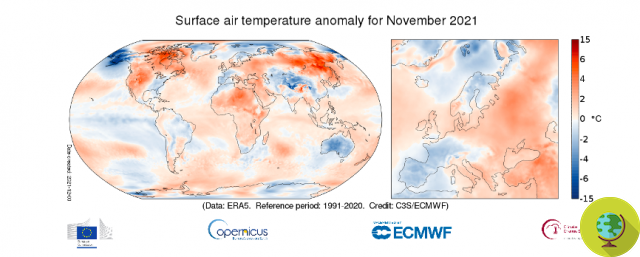
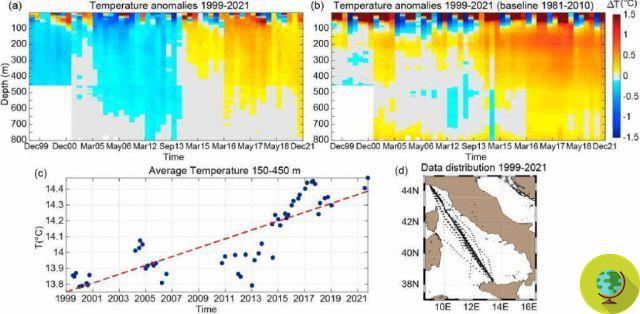
Europe is facing a dark period of increasingly recurring floods, droughts and water shortages: the alarm raised by the latest UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change report
La climate crisis it is not “only” upsetting the balance of our planet, but is inevitably going to impact our lives as well, with increasingly evident consequences. The second volume of the report of theIPCC, the United Nations body monitors climate change.
In the report, just published, several side effects of the phenomenon are addressed, which we can no longer ignore, in particular the drought that will affect more and more in some areas of the Earth and the rise in sea level. And Europe is by no means exempt from these catastrophic consequences, indeed the risks facing the peoples of the Old Continent are numerous.
IPCC Press Conference – Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation & Vulnerability
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability, the Working Group II contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report.#IPCC#ClimateReport
Posted by IPCC on Tuesday, February 22, 2022
Compared to previous editions of the Report, the IPCC today presents a greater effort of integration between the natural, social and economic sciences, highlights the role of social justice, of the knowledge possessed by indigenous peoples and local communities, and offers a
reflection on the fact that immediate and urgent action is important to successfully face the risks posed by the increase in the average temperature of the planet. - the document reads - In many regions, the ability to adapt is already considerably limited. If the temperature increase compared to pre-industrial values exceeds 1,5 ° C, this adaptability will be even more limited and will have an even lower effectiveness.
Index
The main risks facing Europe
In the report, 4 macro risk categories have been identified for Europe. Of course, the level of each risk rises as the level of global warming increases. Therefore these risks become more serious with a 2 ° C warming compared to a 1,5 ° C increase in temperature.
Here are the risks our continent faces:
● Heat waves that put populations and ecosystems at risk: according to the document, the number of deaths and people at risk of heat stress will double or triple if the temperature rises by 3 ° C, compared to 1,5 ° C. Warming will reduce suitable habitats for current terrestrial and marine ecosystems and irreversibly disrupt them.
The measures of adaptation to the thermal stress of the population and the containment of risks from heat waves require multiple interventions on buildings and urban spaces. - experts explain - These measures must be anticipated in southern Europe, where the
risk is greater than in areas further north.
● Serious losses for agriculture: the UN team of experts predicts substantial losses in agricultural production for most areas of Europe in the XNUMXst century due to heat and drought.
● Water resources increasingly scarce: another side effect to consider is that of the scarcity of water resources. In southern Europe the risk is already very high for a level of global warming of 1,5 ° C and increases in the case
of a rise of 3 ° C.
In these regions, the demand for water resources already exceeds what is available today. - reads the report - This gap is widening due to climate change and socio-economic developments. In the event of a temperature rise of 3 ° C, the risk of water scarcity becomes high also in central-western Europe.
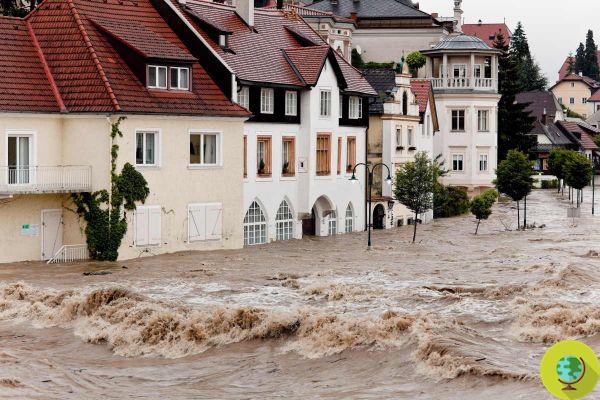
● More frequent and intense floods: due to the climate crisis and the consequent rise in sea level, coastal, river and rainwater floods will be more and more frequent in various areas of Europe.
Read also: The climate crisis hits Europe hard: floods cause deaths and incalculable damage
Mediterranean: the dangerous rise in sea level
One of the areas in which the consequences of global warming will be most palpable is the basin of Mediterranean. The level of our sea, in fact, has already risen by 1,4mm per year during the twentieth century. An increase that has gradually accelerated and will continue at an ever-faster pace if we fail to concretely tackle the climate crisis.
It is expected to continue to grow in the future at a rate similar to the global average, potentially reaching values close to one meter in 2100 in the event of a high level of emissions. - the report warns - The rise in sea level will continue in the coming centuries even if the concentrations of greenhouse gases stabilize. Sea level rise already has an impact on the Mediterranean coasts and will increase the risks of coastal flooding, erosion and salinisation in the future. Narrow sandy shores which are of great value to coastal ecosystems and tourism are at risk of disappearing. The adaptation includes engineering works (of varying scale) and soft / ecosystem systems, as well as the setback of the coastline. Despite their efficiency, engineering works have negative effects on ecosystems, on the tourist attractiveness of the coasts and on economic-financial costs, which make them advantageous only for densely populated areas.
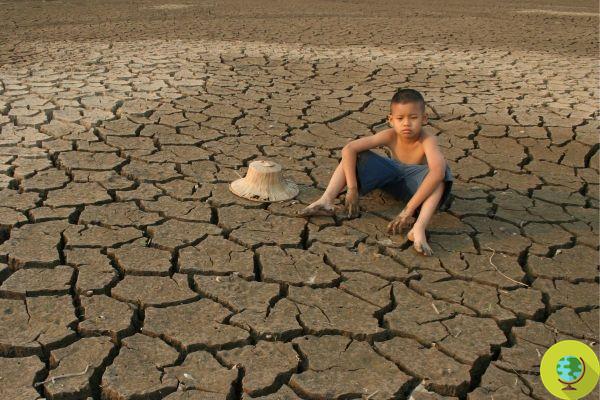
Mediterranean basin increasingly arid
And if on the one hand the floods will be more recurrent in the Mediterranean countries, on the other this area will be increasingly arid. A situation that will have serious repercussions on biodiversity, agriculture and consequently on food systems.
In southern Europe, the number of days with insufficient water resources (availability below demand) and drought increases in all global warming scenarios. - United Nations experts clarify - In the prospect of a global temperature increase of 1,5 ° C and 2 ° C, water scarcity affects, respectively, 18% and 54% of the population. Similarly, soil aridity increases with increasing global warming: in a 3 ° C temperature rise scenario, soil dryness is 40% higher than in a 1,5 ° temperature rise scenario. C.
With warming 3 ° C above pre-industrial levels, it is estimated that 170 million people will be affected by extreme drought. If global warming falls within 1,5 ° C, the population exposed to drought would drop to 120 million.
What can be done to counter this serious phenomenon? As suggested in the report, one idea might be to focus on reforestation. In fact, trees help regulate the flow of water and water resources. Furthermore, one could focus more on agriculture
agriculture based on foods that need a reduced water requirement, for example potatoes.
The one that has just arrived from the new IPCC report is just yet another document that throws the nefarious effects of the climate crisis in our face. How many other reports do we still have to wait before starting to act for the good of the Planet and its inhabitants?
Follow us on Telegram | Instagram | Facebook | TikTok | Youtube
Source: IPCC
Read also:
- Earth will truly be like The Day After Tomorrow: all the similarities between the latest UN report and the film
- The final showdown is near and no one will be saved: the new IPCC report is about to arrive
- "Climate out of control" according to the WWF: hurricanes and cyclones will be more and more frequent
- The Great Barrier Reef faces new mass bleaching due to record heat
- The climate crisis brings record snowfall to the desert