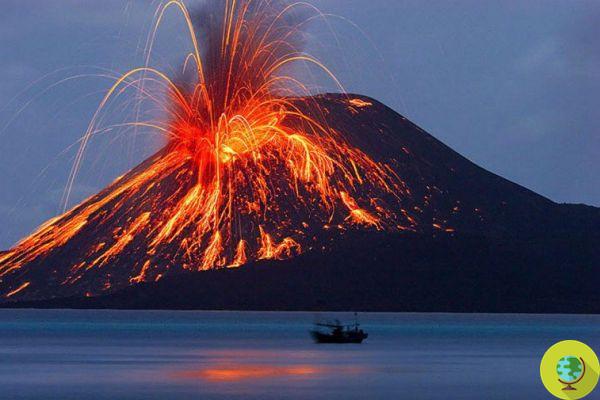
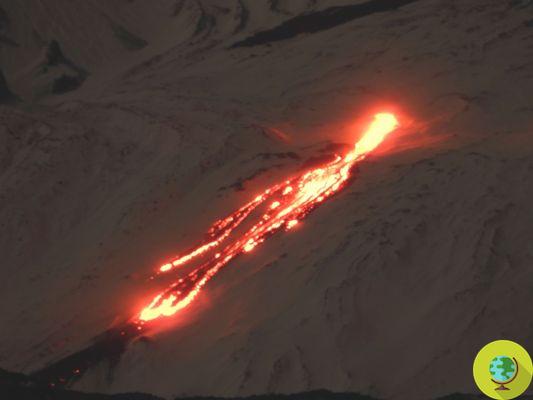
Predict the eruption of a volcano by looking inside it. It is the intuition of some American scholars that the density of the magma contained in the heart of a volcano is the main indicator to be taken into consideration to predict an eruption.
He is about to end up run over, his mother saves him
Predict theeruption of a volcano looking inside. It is the intuition of some American scholars that the density of the magma contained in the heart of a volcano is the main indicator to be taken into consideration to predict an eruption.
The results, published on Nature, come from a detailed study by American researchers Kari Cooper, of the University of California at Davis, and Adam Kent, of the University of Oregon carried out on Mount Hood, an active volcano located in Oregon, and its huge masses of magma which, at very high temperatures, become largely liquid and therefore able to move very easily.
In particular, the researchers examined the two different eruptions of 220 years ago and about 1.500 years ago ei crystals that formed over time in the magma chamber and are now able to provide a chronology and history of temperature. The magma, in fact, is constantly changing its chemical and physical characteristics as it cools and crystallizes, since it exchanges heat with colder rocks.
By analyzing the materials produced by the volcano's last two eruptions, they found that for most of the time it is stored in the volcano, the magma has a very dense and viscous state. This type of condition persists for tens of thousands of years, but in a very short period it can change. The influx of new magma can in fact raise the temperature of the magma already present in the magma chamber making it less viscous, therefore more mobile and at risk of eruption. Precisely this condition, very rare and lasting only two months, is ideal for the volcano to awaken and begin to erupt.
“Our expectation is that there are many volcanoes that behave this way,” says Kari Cooper, a geochemist.
According to an analysis of the crystals, Mount Hood's cold magma reservoir is located about 4-5 kilometers below the surface and its temperature is usually 750 degrees Centigrade. Cooper and research coator Adam Kent think the magma stored under Mount Hood moves rapidly from cold to hot. "We can see the reaction of chemical traces of new magma and calculate the eruption time in days or weeks or maybe months", he concluded Cooper.
Is this really expected an eruption? The authors of the research are cautious for now, but their intent is to collect further data with similar research on other volcanoes. Also because, in fact, there are still no techniques capable of recognizing the transformations that take place in the magma chamber.
Germana Carillo
Photo: Mount Hood, credit Erik Klemetti
READ also:
- Tamu, discovered in the Pacific on volcano larger than Earth
- In Indonesia the volcano which produces blue lava
- The strange phenomenon of the volcano with the shadow on the sky
- A chain of 12 active underwater volcanoes is discovered in Antarctica