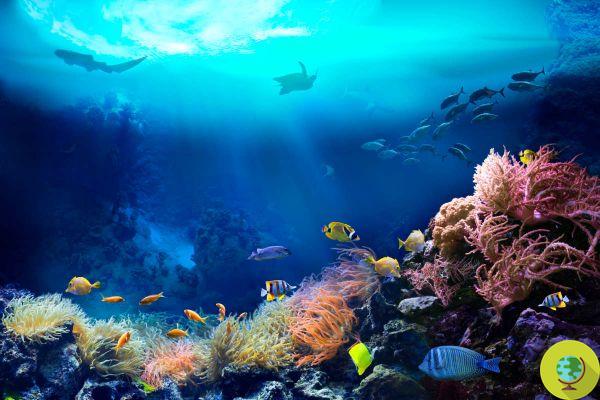
The sea ice of Antarctica is shrinking more and more as a result of the climate crisis, with dramatic consequences for the planet
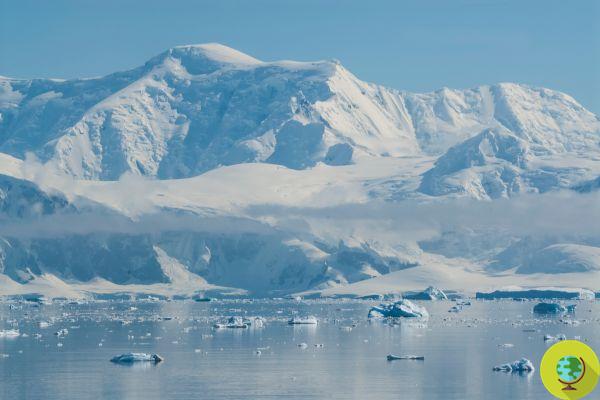
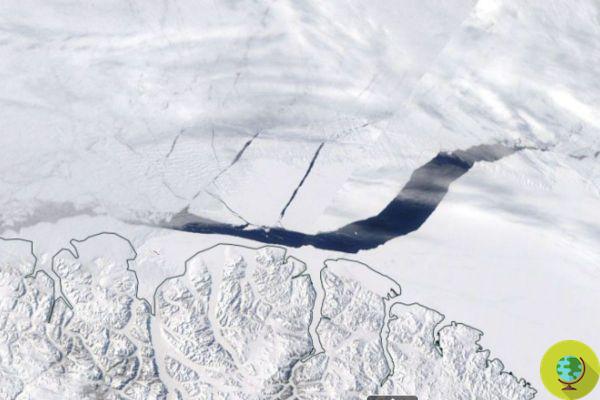
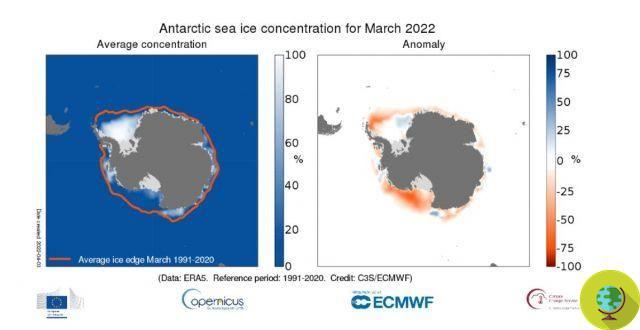
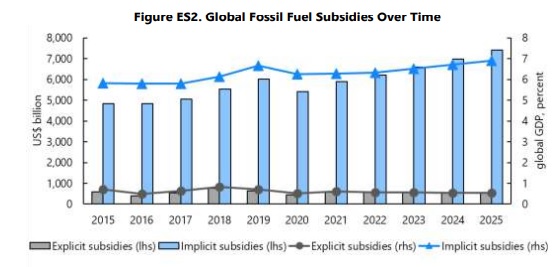
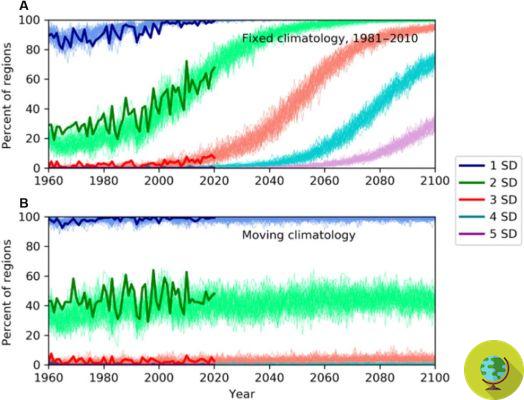
He is about to end up run over, his mother saves himNew and dramatic news comes from the glaciers of Antarctica, increasingly threatened by the consequences of the ongoing climate crisis. On 25 February, the extent of sea ice in the region hit a new record, falling below two million square kilometers - 0,17 million square kilometers less than its last record low five years ago (2017 ).
Since the start of satellite observations of the area, it is the first time that an area of less than two million square kilometers has been recorded: according to scientists, alarmed by these new data, this could be the confirmation that the frozen continent of the Earth is in reality much more sensitive to climate change than previously believed.
Now a new study conducted by researchers at Sun Yat-sen University (in China) tries to clarify the dynamics underlying this worrying decrease in the glacial surface of Antarctica. While it is true that the displacements that occur in the mass of ice play a role in this process, most of the responsibility is attributable to changes in temperature, which are much more felt at the Poles.
In fact, it is estimated that, both at the North Pole and at the South Pole, the increase in average temperatures compared to pre-industrial levels is three times faster than what happens in the rest of the world. The Antarctic continent experienced its first heat wave in 2020, with an unprecedented temperature (+ 9.2 ° C above the maximum average for the period).
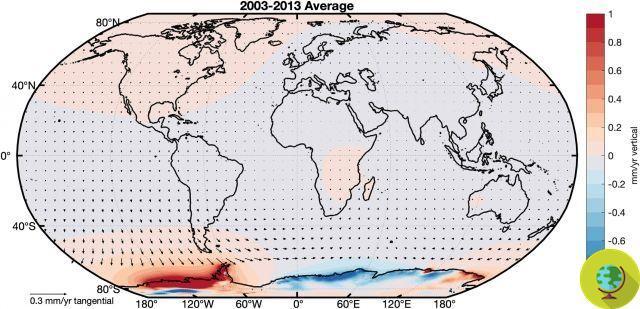
Unlike the Arctic, whose ice surface has "only" decreased by 3% per year since the late 70s, Antarctica has undergone more significant reductions in its total surface area - particularly in the western, most vulnerable to the effects of global warming than the eastern one (which continues to maintain a larger area).
(Read also: The climate crisis is turning Greenland into the largest dam in the world, producing energy to self-destruct)
What are the consequences?
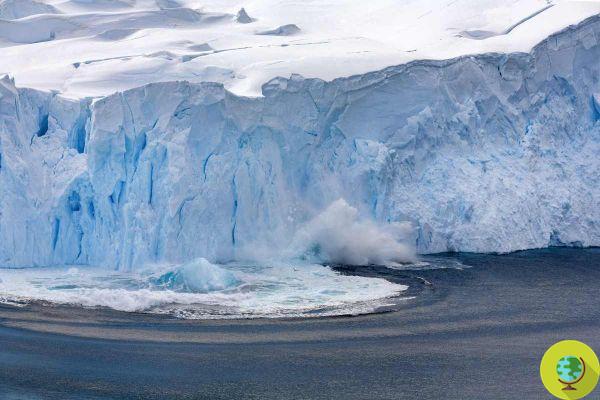
Sea ice melting does not have a direct impact on world sea level rise, as it is ice that already occupies space within ocean waters. However, the relentless process of melting Antarctic glaciers has another, and very worrying, effect in the aggravation of the ongoing climate crisis, according to Chinese researchers.
The frozen surface, by its nature of a whitish color, plays an important "reflecting" action of the Sun's rays, which helps to limit the effects of the star's heat in our atmosphere. If the ice melts and turns into a darker colored liquid mass, the reflective action is clearly less and more energy will be absorbed by the sea water in the form of heat.
Rising sea temperatures cause a ripple effect, which causes sea ice to melt faster, which in turn causes greater heat absorption in an endless vicious circle. Consider that glaciers are able to reflect more than 80% of the energy coming from the Sun, and that ocean waters absorb more or less the same amount of heat.
Follow your Telegram | Instagram | Facebook | TikTok | Youtube
Fonte: Advances in Atmospheric Sciences
We also recommend:
- Melting of glaciers at a record rate. In just 20 years, an area the size of the UK has been lost
- 2021 was the fifth hottest year of all time
- This video shows the dramatic melting of an Icelandic glacier in just 40 days